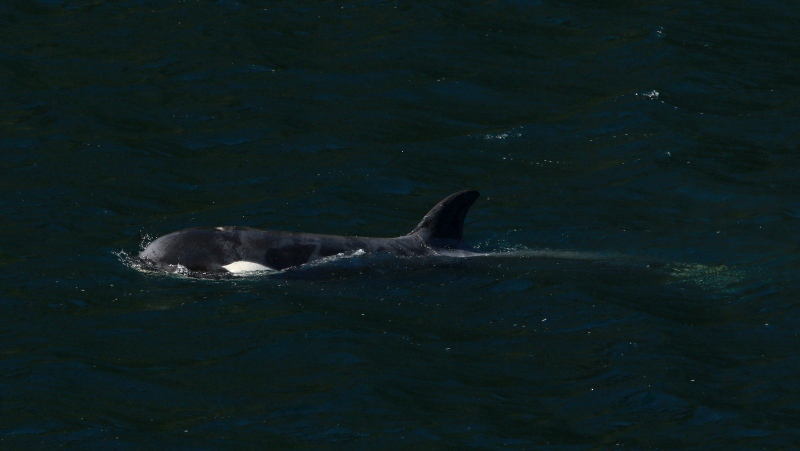

Orca calf that was trapped in B.C. lagoon for weeks swims free
An orca whale calf that has been stranded in a B.C. lagoon for weeks after her pregnant mother died swam out on her own early Friday morning.
An experimental vaccine provided broad protection against all 20 known influenza A and B virus subtypes in initial tests in mice and ferrets, potentially opening a pathway to a universal flu shot that might help prevent future pandemics, according to a U.S. study published on Thursday.
The two-dose vaccine employs the same messenger RNA (mRNA)technology used in the COVID-19 shots developed by Pfizer PFE.N with BioNTech 22UAy.DE, and by Moderna MRNA.O. It delivers tiny lipid particles containing mRNA instructions for cells to create replicas of so-called hemagglutinin proteins that appear on influenza virus surfaces.
A universal vaccine would not mean an end to flu seasons, but would replace the guess work that goes into developing annual shots months ahead of flu season each year.
"The idea here is to have a vaccine that will give people a baseline level of immune memory to diverse flu strains, so that there will be far less disease and death when the next flu pandemic occurs," study leader Scott Hensley of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania said in a statement.
Unlike standard flu vaccines that deliver one or two versions of hemagglutinin, the experimental vaccine includes 20 different types in the hope of getting the immune system to recognize any flu virus it might encounter in the future.
In lab experiments, vaccinated animals' immune systems recognized the hemagglutinin proteins and defended against 18 different strains of influenza A and two strains of influenza B. Antibody levels induced by the vaccine remained unchanged for at least four months, according to a report published in the journal Science.
The vaccine reduced signs of illness and protected from death even when the ferrets were exposed to a different type of flu not in the vaccine, the researchers said.
Moderna and Pfizer both have mRNA flu vaccines in late-stage human trials, and GSK GSK.L and partner CureVac 5CV.DE are testing an mRNA flu vaccine in an early-stage safety trial in humans. These vaccines are designed to defend against only four recently-circulating influenza strains but could theoretically be changed up each year.
The universal flu vaccine, if successful in human trials, would not necessarily prevent infection. The goal is to provide durable protection against severe disease and death, Hensley said.
Questions remain regarding how to judge efficacy and potential regulatory requirements for a vaccine against possible future viruses that are not currently circulating, Alyson Kelvin and Darryl Falzarano of the University of Saskatchewan, Canada, wrote in a commentary published with the study.
While the promising results with the new vaccine "suggest a protective capacity against all subtypes of influenza viruses, we cannot be sure until clinical trials in volunteers are done," Adolfo García-Sastrem, director of the Institute for Global Health and Emerging Pathogens at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, said in a statement.
Reporting by Nancy Lapid; Editing by Christine Soares and Bill Berkrot

An orca whale calf that has been stranded in a B.C. lagoon for weeks after her pregnant mother died swam out on her own early Friday morning.
King Charles III’s doctors are 'sufficiently pleased' with his cancer treatment and he is expected to return to public-facing duties, Buckingham Palace announced on Friday.
After the Assembly of First Nations' national chief complained to Air Canada about how staffers treated her and her ceremonial headdress on a flight this week, she says the airline responded by offering a 15 per cent discount on her next flight.
Sophie Gregoire Trudeau says there is 'still so much love' between her and Prime Minister Justin Trudeau, as they navigate their post-separation relationship co-parenting their three children.
The current overall public health risk posed by the H5N1 bird flu virus is low, the World Health Organization said on Friday, but urged countries to stay alert for cases of animal-to-human transmission.
Philadelphia 76ers All-Star centre Joel Embiid has been diagnosed with Bell’s palsy, a form of facial paralysis he says has affected him since before the play-in tournament.
An idyllic 453-acre private island is up for sale off the west coast of Scotland and it comes with sandy beaches, puffins galore, seven houses, a pub, a helipad and a flock of black-faced sheep.
An investigation is underway after a Regina police officer was accidentally shot by a fellow officer’s gun during the search of a house early Friday morning.
A pair of Montreal designers' work has now been viewed over 41 million times. Taylor Swift dons a Victorian throwback black gown in her latest music video, 'Fortnight', designed by UNTTLD due Simon Belanger and Jose Manuel Saint-Jacques.
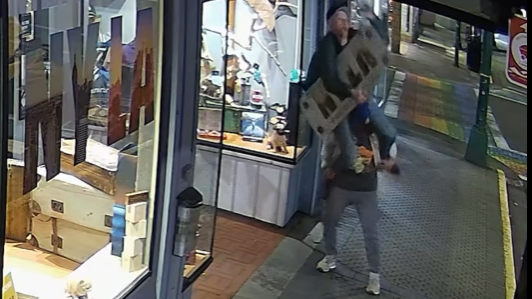
Mounties in Nanaimo, B.C., say two late-night revellers are lucky their allegedly drunken antics weren't reported to police after security cameras captured the men trying to steal a heavy sign from a downtown business.
A property tax bill is perplexing a small townhouse community in Fergus, Ont.
When identical twin sisters Kim and Michelle Krezonoski were invited to compete against some of the world’s most elite female runners at last week’s Boston Marathon, they were in disbelief.
The giant stone statues guarding the Lions Gate Bridge have been dressed in custom Vancouver Canucks jerseys as the NHL playoffs get underway.
A local Oilers fan is hoping to see his team cut through the postseason, so he can cut his hair.
A family from Laval, Que. is looking for answers... and their father's body. He died on vacation in Cuba and authorities sent someone else's body back to Canada.
A former educational assistant is calling attention to the rising violence in Alberta's classrooms.
The federal government says its plan to increase taxes on capital gains is aimed at wealthy Canadians to achieve “tax fairness.”
At 6'8" and 350 pounds, there is nothing typical about UBC offensive lineman Giovanni Manu, who was born in Tonga and went to high school in Pitt Meadows.