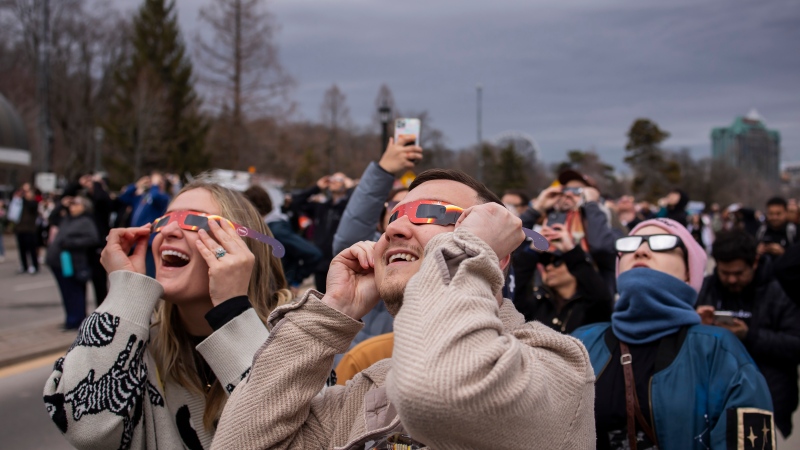

More than 115 cases of eye damage reported in Ontario after solar eclipse
More than 115 people who viewed the solar eclipse in Ontario earlier this month experienced eye damage after the event, according to eye doctors in the province.
More than 5,000 new species have been discovered at an expansive future deep-sea mining site in the Pacific Ocean.
Known as the Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ), the mineral-rich site stretches six million square kilometers from Mexico to Hawaii. About twice the size of India, the CCZ has already been carved up into mining claims for future exploitation, with companies eager to harvest abundant deposits of key battery materials like manganese and cobalt that are located 4,000 to 6,000 metres below the surface.
To better understand what could be at risk once mining begins, a team of biologists led by London's Natural History Museum sought to survey the region's biodiversity. Of the 5,578 species they identified, approximately 90 per cent were entirely new to science.
"We share this planet with all this amazing biodiversity, and we have a responsibility to understand it and protect it," lead author and Natural History Museum deep-sea ecologist Muriel Rabone said in a news release last week.
The team compiled a list of all species found in previous studies of the region, and also embarked on their own research expeditions to survey the ocean floor. Using techniques like remote-controlled vehicles and box core sampling, which is basically a box that scoops up material from the seafloor, they collected over 100,000 records of creatures of the deep from this largely untouched underwater wilderness.
“It's a big boat, but it feels tiny in the middle of the ocean,” Rabone said of the research cruises. “And it was amazing—in every single box core sample, we would see new species.”
The most common types of animals were arthropods, echinoderms, worms and sponges. Newly discovered species included what's known as the "gummy squirrel," a gelatinous-looking sea cucumber with a large tail-like protrusion. Only six species have been seen elsewhere in the ocean.
"Some of the sponges look like classic bath sponges, and some look like vases. They’re just beautiful," Rabone said. "One of my favorites is the glass sponges. They have these little spines, and under the microscope, they look like tiny chandeliers or little sculptures."
The peer-reviewed study, which includes images, was published in the journal Current Biology last week.
The UN-affiliated International Seabed Authority, which was created to regulate mining in international waters, begins accepting applications to exploit the CCZ in July. Commercial deep-sea mining, which is still in an exploratory phase, would collect potato-sized deposits known as "polymetallic nodules" that can be found on and just under the region's seabed.
"There are so many wonderful species in the CCZ, and with the possibility of mining looming, it’s doubly important that we know more about these really understudied habitats," Rabone said.
While companies and countries like China and the U.S. pursue deep-sea mining, others like France, Chile and Canada have called for moratoriums or bans in their waters over environmental concerns.
With files from Reuters

More than 115 people who viewed the solar eclipse in Ontario earlier this month experienced eye damage after the event, according to eye doctors in the province.
The B.C. NDP has asked the federal government to recriminalize public drug use, marking a major shift in the province's approach to addressing the deadly overdose crisis.
George Mallory is renowned for being one of the first British mountaineers to attempt to scale the dizzying heights of Mount Everest during the 1920s. Nearly a century later, newly digitized letters shed light on Mallory’s hopes and fears about ascending Everest.
An orca whale calf that has been stranded in a B.C. lagoon for weeks after her pregnant mother died swam out on her own early Friday morning.
Sophie Gregoire Trudeau says there is 'still so much love' between her and Prime Minister Justin Trudeau, as they navigate their post-separation relationship co-parenting their three children.
An Ontario man who took out a loan to pay for auto repairs said his car was repossessed after he missed two payments.
Devastating tornadoes tore across parts of eastern Nebraska and northeast Texas Friday as a multi-day severe thunderstorm event ramped up in the central United States, injuring at least three people.
A Sherwood Park family says their new house is uninhabitable. The McNaughton's say they were forced to leave the house after living there for only a week because contaminants inside made it difficult to breathe.
Donald Trump's defence team attacked the credibility Friday of the prosecution's first witness in his hush money case, seeking to discredit testimony detailing a scheme between Trump and a tabloid to bury negative stories to protect the Republican's 2016 presidential campaign.
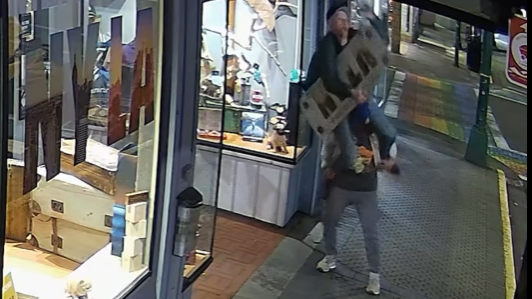
Mounties in Nanaimo, B.C., say two late-night revellers are lucky their allegedly drunken antics weren't reported to police after security cameras captured the men trying to steal a heavy sign from a downtown business.
A property tax bill is perplexing a small townhouse community in Fergus, Ont.
When identical twin sisters Kim and Michelle Krezonoski were invited to compete against some of the world’s most elite female runners at last week’s Boston Marathon, they were in disbelief.
The giant stone statues guarding the Lions Gate Bridge have been dressed in custom Vancouver Canucks jerseys as the NHL playoffs get underway.
A local Oilers fan is hoping to see his team cut through the postseason, so he can cut his hair.
A family from Laval, Que. is looking for answers... and their father's body. He died on vacation in Cuba and authorities sent someone else's body back to Canada.
A former educational assistant is calling attention to the rising violence in Alberta's classrooms.
The federal government says its plan to increase taxes on capital gains is aimed at wealthy Canadians to achieve “tax fairness.”
At 6'8" and 350 pounds, there is nothing typical about UBC offensive lineman Giovanni Manu, who was born in Tonga and went to high school in Pitt Meadows.
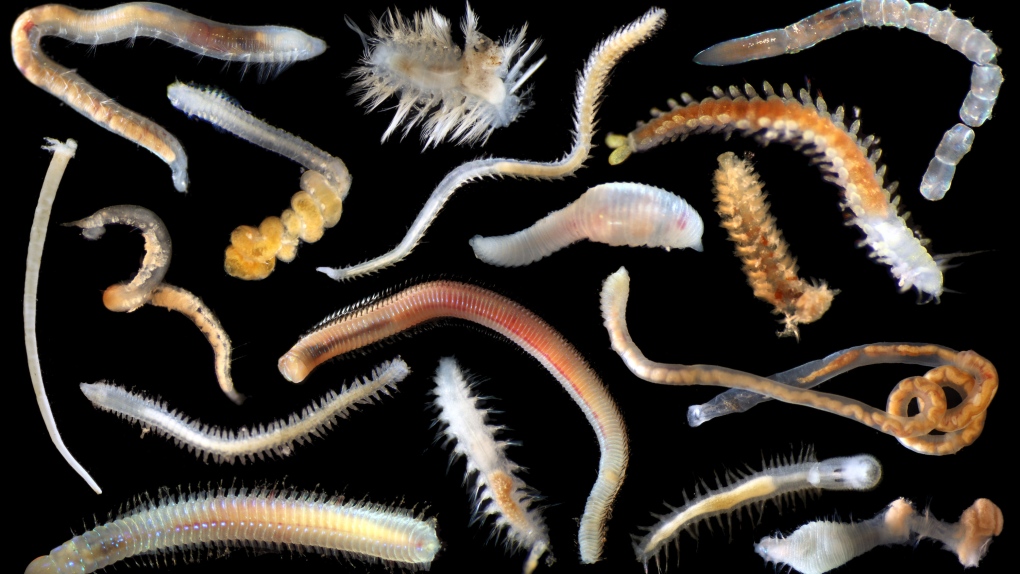 More than 5,000 new species have been discovered at an expansive future deep-sea mining site in the Pacific Ocean. (SMARTEX Project, Natural Environment Research Council, UK)
More than 5,000 new species have been discovered at an expansive future deep-sea mining site in the Pacific Ocean. (SMARTEX Project, Natural Environment Research Council, UK)