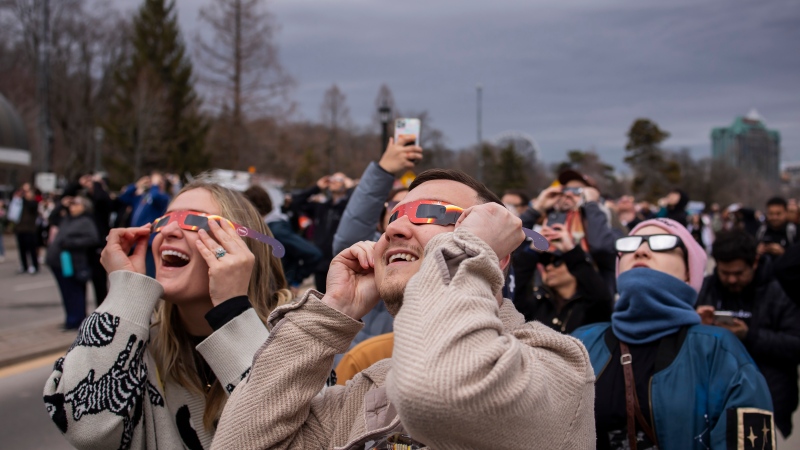

More than 115 cases of eye damage reported in Ontario after solar eclipse
More than 115 people who viewed the solar eclipse in Ontario earlier this month experienced eye damage after the event, according to eye doctors in the province.
Tech billionaire Elon Musk said his Neuralink company is seeking permission to test its brain implant in people soon.
In a "show and tell" presentation livestreamed Wednesday night, Musk said his team is in the process of asking U.S. regulators to allow them to test the device. He said he thinks the company should be able to put the implant in a human brain as part of a clinical trial in about six months, though that timeline is far from certain.
Musk's Neuralink is one of many groups working on linking brains to computers, efforts aimed at helping treat brain disorders, overcoming brain injuries and other applications.
The field dates back to the 1960s, said Rajesh Rao, co-director of the Center for Neurotechnology at the University of Washington. "But it really took off in the 90s. And more recently we've seen lots of advances, especially in the area of communication brain computer interfaces."
Rao, who watched Musk's presentation online, said he doesn't think Neuralink is ahead of the pack in terms of brain-computer interface achievements. "But ... they are quite ahead in terms of the actual hardware in the devices," he said.
The Neuralink device is about the size of a large coin and is designed to be implanted in the skull, with ultra-thin wires going directly into the brain. Musk said the first two applications in people would be restoring vision and helping people with little or no ability to operate their muscles rapidly use digital devices.
He said he also envisions that in someone with a broken neck, signals from the brain could be bridged to Neuralink devices in the spinal cord.
"We're confident there are no physical limitations to enabling full body functionality," said Musk, who recently took over Twitter and is the CEO of Tesla and SpaceX.
In experiments by other teams, implanted sensors have let paralyzed people use brain signals to operate computers and move robotic arms. In a 2018 study in the journal PLOS ONE, three participants with paralysis below the neck affecting all of their limbs used an experimental brain-computer interface being tested by the consortium BrainGate. The interface records neural activity from a small sensor in the brain to navigate things like email and apps.
A recent study in the journal Nature, by scientists at the Swiss research center NeuroRestore, identified a type of neuron activated by electrical stimulation of the spinal cord, allowing nine patients with chronic spinal cord injury to walk again.
Researchers have also been working on brain and machine interfaces for restoring vision. Rao said some companies have developed retinal implants, but Musk's announcement suggested his team would use signals directly targeting the brain's visual cortex, an approach that some academic groups are also pursuing, "with limited success."
Neuralink spokespeople did not immediately respond to an email to the press office. Dr. Jaimie Henderson, a neurosurgery professor at Stanford University who is an adviser for Neuralink, said one-way Neuralink is different than some other devices is that it has the ability to reach into deeper layers of the brain. But he added: "There are lots of different systems that have lots of different advantages."
------
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute's Science and Educational Media Group. The AP is solely responsible for all content.

More than 115 people who viewed the solar eclipse in Ontario earlier this month experienced eye damage after the event, according to eye doctors in the province.
George Mallory is renowned for being one of the first British mountaineers to attempt to scale the dizzying heights of Mount Everest during the 1920s. Nearly a century later, newly digitized letters shed light on Mallory’s hopes and fears about ascending Everest.
A Sherwood Park family says their new house is uninhabitable. The McNaughton's say they were forced to leave the house after living there for only a week because contaminants inside made it difficult to breathe.
A man has been handed a lengthy hunting ban and fined thousands of dollars for illegally killing a grizzly bear, B.C. conservation officers say.
The B.C. NDP has asked the federal government to recriminalize public drug use, marking a major shift in the province's approach to addressing the deadly overdose crisis.
Sophie Gregoire Trudeau says there is 'still so much love' between her and Prime Minister Justin Trudeau, as they navigate their post-separation relationship co-parenting their three children.
An emergency slide fell off a Delta Air Lines jetliner shortly after takeoff Friday from New York, and pilots who felt a vibration in the plane circled back to land safely at JFK Airport.
The Ontario Provincial Police (OPP) says it's investigating an interaction between a uniformed officer and anti-Trudeau government protestors after a video circulated on social media.
An Ontario man who took out a loan to pay for auto repairs said his car was repossessed after he missed two payments.
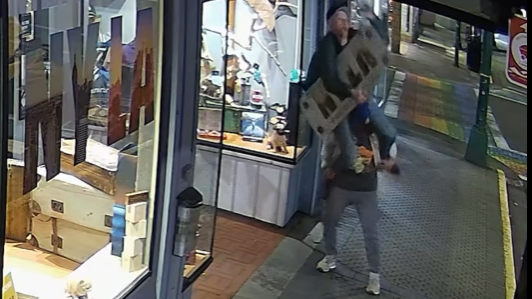
Mounties in Nanaimo, B.C., say two late-night revellers are lucky their allegedly drunken antics weren't reported to police after security cameras captured the men trying to steal a heavy sign from a downtown business.
A property tax bill is perplexing a small townhouse community in Fergus, Ont.
When identical twin sisters Kim and Michelle Krezonoski were invited to compete against some of the world’s most elite female runners at last week’s Boston Marathon, they were in disbelief.
The giant stone statues guarding the Lions Gate Bridge have been dressed in custom Vancouver Canucks jerseys as the NHL playoffs get underway.
A local Oilers fan is hoping to see his team cut through the postseason, so he can cut his hair.
A family from Laval, Que. is looking for answers... and their father's body. He died on vacation in Cuba and authorities sent someone else's body back to Canada.
A former educational assistant is calling attention to the rising violence in Alberta's classrooms.
The federal government says its plan to increase taxes on capital gains is aimed at wealthy Canadians to achieve “tax fairness.”
At 6'8" and 350 pounds, there is nothing typical about UBC offensive lineman Giovanni Manu, who was born in Tonga and went to high school in Pitt Meadows.
 FILE - In this Sunday, Jan. 19, 2020. file photo, Elon Musk founder, CEO, and chief engineer/designer of SpaceX speaks during a news conference after a Falcon 9 SpaceX rocket test flight to demonstrate the capsule's emergency escape system at the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Fla. Elon Musk is not content with just electric cars, populating Mars and building underground tunnels to solve traffic problems. He also wants to get inside your brain. His startup, Neuralink, wants to one day implant computer chips inside people's brain. (AP Photo/John Raoux, File)
FILE - In this Sunday, Jan. 19, 2020. file photo, Elon Musk founder, CEO, and chief engineer/designer of SpaceX speaks during a news conference after a Falcon 9 SpaceX rocket test flight to demonstrate the capsule's emergency escape system at the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Fla. Elon Musk is not content with just electric cars, populating Mars and building underground tunnels to solve traffic problems. He also wants to get inside your brain. His startup, Neuralink, wants to one day implant computer chips inside people's brain. (AP Photo/John Raoux, File)