
B.C. tenants evicted for landlord's use after refusing large rent increase to take over neighbouring suite
Ashley Dickey and her mother rented part of the same Coquitlam duplex in three different decades under three different landlords.
As artificial intelligence software and advanced computers revolutionize modern technology, some researchers see a future where computer programmers leap from silicon to organic molecules.
Scientists with Johns Hopkins University are investigating the possibility of “biocomputers” – programs modelled from organic molecules such as human DNA or proteins – unlocking new insights on human biology and advancing the processing power of future tech.
Much of these technological anticipations derive from something called “organoids,” which are lab-grown tissues resembling fully grown organs, sharing similar biological complexities to tissues comprised in kidneys, lungs and brain cells.
Organoids, which have become more prominent in labs over the last two decades, currently offer scientists a more ethical alternative to animal or human testing, mimicking basic functions of cells and advancing scientific understandings towards how those cells operate.
Most recently, scientists with Johns Hopkins have been assessing the nature of “brain organoids,” which are orbs the size of a pen dot that mirror the basic neural functions of learning and remembering in the human brain, according to a news release.
“This opens up research on how the human brain works,” Thomas Hartung, a professor of environmental health sciences at Johns Hopkins, said in the release, adding that deeper insights into human cognition can also serve as a roadmap for unlocking greater computing power in future technology.
“Computing and artificial intelligence have been driving the technology revolution but they are reaching a ceiling,” he said. “Biocomputing is an enormous effort of compacting computational power and increasing its efficiency to push past our current technological limits.”
Hartung and his team first began growing brain organoids in 2012 by using cells from human skin samples that they reprogrammed to multiply and mirror the functions of other cells. Each of these organoids consist of approximately 50,000 cells, and Hartung and his team envision building a futuristic computer that uses the organization of these cells as a basis for new forms of computer programming.
Despite the fact that computer calculations involving numbers and data are far superior to brains in terms of speed and volume, Hartung pointed out that humans are currently more efficient in arriving at complex logical decisions with substantially less processing power required.
For instance, our ability to tell the difference between a cat and a dog based on a quick glance requires much less processing power than a computer program would require, despite the fact that an advance computer would be able to provide way more information on each species than the average person.
Through using the complexity of brain organoids and training them with artificial intelligence, Hartung believes “biocomputers” can reach new computing speed, processing power, storage capabilities, and general data efficiency.
“Computers that run on this ‘biological hardware’ could in the next decade begin to alleviate energy consumption demands of supercomputing that are becoming increasingly unsustainable,” he said.
He added that it could be decades before an organoid-based computer would effectively function, but that the possibility remains as the field of organoid research expands.
Lena Smirnova, a Johns Hopkins assistant professor of environmental health and engineering, who is co-leading the investigation, added that such research could revolutionize drug testing research for neurodegeneration and neurodevelopmental disorders.
“The tools we are developing towards biological computing are the same tools that will allow us to understand changes in neuronal networks specific for autism, without having to use animals or to access patients,” she said in the news release. By advancing bio-computing, Smirnova believes researchers can “understand the underlying mechanisms of why patients have these cognition issues and impairments.”
Smirnova and Hartung further outlined their plans for assessing the future of organoid intelligence and bio-computing in the journal Frontiers in Science last month.

Ashley Dickey and her mother rented part of the same Coquitlam duplex in three different decades under three different landlords.
A man who fell into a crevasse while leading a backcountry ski group deep in the Canadian Rockies has died.
A new survey by Dalhousie University's Agri-Food Analytics Lab asked Canadians about their food consumption habits amid rising prices.
MPP Sarah Jama was asked to leave the Legislative Assembly of Ontario by House Speaker Ted Arnott on Thursday for wearing a keffiyeh, a garment which has been banned at Queen’s Park.
Charlie Woods failed to advance in a U.S. Open local qualifying event Thursday, shooting a 9-over 81 at Legacy Golf & Tennis Club.
As Donald Trump was running for president in 2016, his old friend at the National Enquirer was scooping up potentially damaging stories about the candidate and paying out tens of thousands of dollars to keep them from the public eye.
After Prime Minister Justin Trudeau said the federal government would still send Canada Carbon Rebate cheques to Saskatchewan residents, despite Saskatchewan Premier Scott Moe's decision to stop collecting the carbon tax on natural gas or home heating, questions were raised about whether other provinces would follow suit. CTV News reached out across the country and here's what we found out.
A Montreal actress, who has previously detailed incidents she had with disgraced Hollywood producer Harvey Weinstein, says a New York Court of Appeals decision overturning his 2020 rape conviction is 'discouraging' but not surprising.
Caleb Williams is heading to the Windy City, aiming to become the franchise quarterback Chicago has sought for decades.
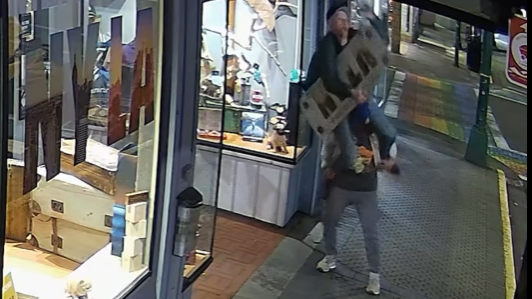
Mounties in Nanaimo, B.C., say two late-night revellers are lucky their allegedly drunken antics weren't reported to police after security cameras captured the men trying to steal a heavy sign from a downtown business.
A property tax bill is perplexing a small townhouse community in Fergus, Ont.
When identical twin sisters Kim and Michelle Krezonoski were invited to compete against some of the world’s most elite female runners at last week’s Boston Marathon, they were in disbelief.
The giant stone statues guarding the Lions Gate Bridge have been dressed in custom Vancouver Canucks jerseys as the NHL playoffs get underway.
A local Oilers fan is hoping to see his team cut through the postseason, so he can cut his hair.
A family from Laval, Que. is looking for answers... and their father's body. He died on vacation in Cuba and authorities sent someone else's body back to Canada.
A former educational assistant is calling attention to the rising violence in Alberta's classrooms.
The federal government says its plan to increase taxes on capital gains is aimed at wealthy Canadians to achieve “tax fairness.”
At 6'8" and 350 pounds, there is nothing typical about UBC offensive lineman Giovanni Manu, who was born in Tonga and went to high school in Pitt Meadows.
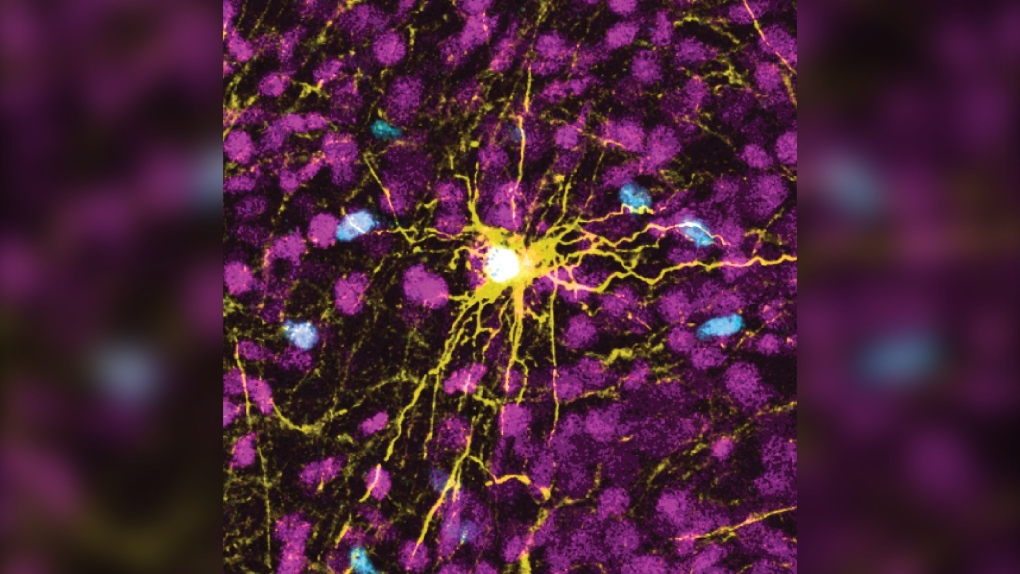 This microscope image provided by Pasca Lab/Stanford Medicine shows a human astrocyte cell, center in yellow, and human glial cells (scattered in blue) inside the brain of a rat. (Pasca Lab/Stanford Medicine via AP)
This microscope image provided by Pasca Lab/Stanford Medicine shows a human astrocyte cell, center in yellow, and human glial cells (scattered in blue) inside the brain of a rat. (Pasca Lab/Stanford Medicine via AP)