
B.C. tenants evicted for landlord's use after refusing large rent increase to take over neighbouring suite
Ashley Dickey and her mother rented part of the same Coquitlam duplex in three different decades under three different landlords.
A new peer-reviewed study from the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) report in Brain Connectivity has found individualized brain “fingerprints” which can help diagnose early Alzheimer's Disease (AD) in pre-symptomatic patients.
Using an innovative brain imaging technique, the neuroscientists conducting the research could visualize subtle brain changes in pre-symptomatic Alzheimer's patients, which could help determine how the disease begins and progresses.
“Prior studies have not found an association between brain function and behavior in preclinical AD,” said Andreana Benitez, Ph.D., one of the study researchers, in a press release. “Using these individualized maps of brain function, we found a potential brain-based reason for very subtle cognitive changes in this early phase of the disease.”
The team used a new technique called “the individualized functional connectome” which was developed by their collaborator, Hesheng Liu, Ph.D, to analyze the brain images.
This highly sensitive technique is able to show unique brain patterns for each individual, something that traditional methods cannot do.
“We all have the same functional parts of our brain, but they're positioned slightly differently, sort of like a fingerprint,” said Stephanie Fountain-Zaragoza, Ph.D, another one of the study researchers, in a press release. “This method creates an individualized brain fingerprint that more accurately reflects where the different functional regions are in each individual’s brain.”
The team of neuroscientists applied this method to a group of 149 research participants, ages 45 to 85, who did not have signs of cognitive decline.
Each of the participants' brains were scanned by a positron emission tomography (PET) scan and divided into groups based on the results—those who showed PET scan evidence of early amyloid-beta protein buildup, and those who did not.
In order for the researchers to have the brain “fingerprints” generated, they also underwent MRI scans.
Using behaviour-based testing, researchers assessed how well the research participants performed cognitively.
What they found was certain changes in the brain fingerprint were associated with those with worse information processing abilities in the participants who had amyloid-beta buildup, or preclinical Alzheimer's.
Conversely, they found information processing was better in those with higher within-network connectivity, or more brain activity within important areas of the brain.
“A healthy brain typically has a balance of connectivity within and between its networks,” said Fountain-Zaragoza. “We found that in preclinical AD—when amyloid build-up is present in the brain—this balance can be disrupted, potentially leading to information no longer being processed as efficiently.”
The study suggests early states of protein buildup in the brain could affect cognitive abilities before the symptoms of cognitive decline become noticeable. Plus, it suggests that changes in connectivity within certain brain networks could signal early issues with information processing abilities, which, according to the researchers, could be an area therapies could target to improve the outcomes for those with Alzheimer's.
This method could improve how preclinical cases of Alzheimer's are studied, particularly as adults with preclinical Alzheimer's don’t have noticeable symptoms of cognitive decline—despite having the earliest signs of disease such as buildup of amyloid-beta proteins in their brain, according to the study.
In the future, the researchers plan to explore how brain changes affect the progression of Alzheimer's as well as potential treatments, as they expand this research.
“There's a lot of great work aimed at helping us understand the earliest signs and symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease,” said Fountain-Zaragoza. “This area of work is important for understanding the full spectrum of the disease and identifying who might be at risk of developing it.”

Ashley Dickey and her mother rented part of the same Coquitlam duplex in three different decades under three different landlords.
A man who fell into a crevasse while leading a backcountry ski group deep in the Canadian Rockies has died.
A new survey by Dalhousie University's Agri-Food Analytics Lab asked Canadians about their food consumption habits amid rising prices.
MPP Sarah Jama was asked to leave the Legislative Assembly of Ontario by House Speaker Ted Arnott on Thursday for wearing a keffiyeh, a garment which has been banned at Queen’s Park.
Charlie Woods failed to advance in a U.S. Open local qualifying event Thursday, shooting a 9-over 81 at Legacy Golf & Tennis Club.
As Donald Trump was running for president in 2016, his old friend at the National Enquirer was scooping up potentially damaging stories about the candidate and paying out tens of thousands of dollars to keep them from the public eye.
After Prime Minister Justin Trudeau said the federal government would still send Canada Carbon Rebate cheques to Saskatchewan residents, despite Saskatchewan Premier Scott Moe's decision to stop collecting the carbon tax on natural gas or home heating, questions were raised about whether other provinces would follow suit. CTV News reached out across the country and here's what we found out.
A Montreal actress, who has previously detailed incidents she had with disgraced Hollywood producer Harvey Weinstein, says a New York Court of Appeals decision overturning his 2020 rape conviction is 'discouraging' but not surprising.
Caleb Williams is heading to the Windy City, aiming to become the franchise quarterback Chicago has sought for decades.
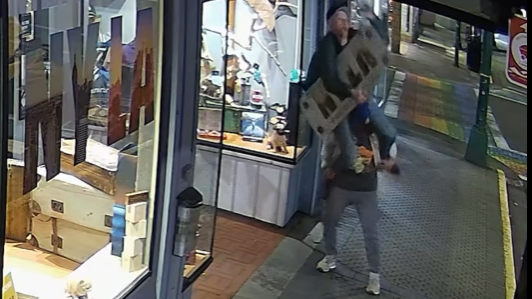
Mounties in Nanaimo, B.C., say two late-night revellers are lucky their allegedly drunken antics weren't reported to police after security cameras captured the men trying to steal a heavy sign from a downtown business.
A property tax bill is perplexing a small townhouse community in Fergus, Ont.
When identical twin sisters Kim and Michelle Krezonoski were invited to compete against some of the world’s most elite female runners at last week’s Boston Marathon, they were in disbelief.
The giant stone statues guarding the Lions Gate Bridge have been dressed in custom Vancouver Canucks jerseys as the NHL playoffs get underway.
A local Oilers fan is hoping to see his team cut through the postseason, so he can cut his hair.
A family from Laval, Que. is looking for answers... and their father's body. He died on vacation in Cuba and authorities sent someone else's body back to Canada.
A former educational assistant is calling attention to the rising violence in Alberta's classrooms.
The federal government says its plan to increase taxes on capital gains is aimed at wealthy Canadians to achieve “tax fairness.”
At 6'8" and 350 pounds, there is nothing typical about UBC offensive lineman Giovanni Manu, who was born in Tonga and went to high school in Pitt Meadows.