
Expert warns of food consumption habits amid rising prices
A new survey by Dalhousie University's Agri-Food Analytics Lab asked Canadians about their food consumption habits amid rising prices.
Omicron’s spread has been so extensive that there are few families that haven’t been touched by it at all -- and for some families, that means worrying about their children.
In the Toronto area, Sarah Bankuti watched as her newborn baby Aviv spent Saturday in hospital suffering with COVID-19.
“Very scary because my daughter, she's 10 weeks old,” she told CTV News. “So she had a fever and she, all yesterday, was just non-stop throwing up.”
Although the baby is home now, she’s still quite ill.
The Bankuti family has taken every precaution during the pandemic as their three-year-old daughter Alice has a brain tumour and is undergoing chemotherapy.
Even though the parents are both vaccinated, COVID-19 crept into the family anyways, infecting everyone in the process.
“That's why COVID is so scary,” Bankuti said. “You don't know how it's going to affect people at all, but especially for our children, we just don't know. For the past 48 hours, we've been so worried.”
She added that they family hasn’t been able to sleep while worrying about their children.
“We don't know what the full side effects are of this,” she said. “It's new still.”
Doctors do know just how transmissible Omicron is, with its whirlwind advance around the globe and scientists worry Omicron won’t be the last version of the virus.
“More and more people are getting infected,” Leonardo Martinez, an assistant professor at Boston University School of Public Health, told CTV News. “The more people that get infected, the more chances there are for new mutations to occur, and that's how new variants come.”
The World Health Organization reported a record 15 million new COVID-19 cases for the week of Jan. 3-9, a 55-per-cent increase from the previous week.
“Those mutations, one change, two changes, doesn't really matter, doesn't take hold, sometimes it does, and that's where we go from a variant of interest to a variant of concern,” said Cynthia Carr, founder and epidemiologist with EPI research incorporated in Winnipeg.
Small changes may bring the pandemic to an endemic phase, according to Dr. Gerald Evans, an infectious disease physician with the Kingston Health Sciences Centre.
“The thing that we're afraid of is the big changes that would produce a new variant with a new Greek letter,” he said.
A new variant may evade immunity better than Omicron, however, and scientists stress the importance of vaccines to reduce hospitalization, death and emerging new variants.
“Mutations are more common in severe and long-lasting COVID infections,” Martinez said. “Therefore, because vaccines prevent severe infections they can also prevent proliferation of new variants.”
All while hopefully creating a circle of protection around those too young to be vaccinated.
“Those would actually protect the people who were unvaccinated because the virus can't get at them because they're surrounded by a whole group of people, in which, infection, and or transmission after being infected is remarkably reduced by the vaccine,” Evans said.
Vaccination rates are fairly high in Canada, but the World Health Organization continues to stress the importance of global vaccine coverage.
Although wealthy countries have been able to acquire an abundance of vaccines, it’s a different story for many other regions. Ninety countries did not reach the target of vaccinating 40 per cent of their populations by the end of last year, and 36 of those countries have not yet vaccinated 10 per cent of their populations.
With files from CTVNews.ca's Alexandra Mae Jones

A new survey by Dalhousie University's Agri-Food Analytics Lab asked Canadians about their food consumption habits amid rising prices.
It was evident to the federal government as early as last fall that Loblaw and Walmart might be holdouts to the grocery code of conduct, jeopardizing the project's success.
Royal commentator Afua Hagan writes that when King Charles recently admitted Catherine to the Order of the Companions of Honour, it not only made history, but it reinforced the strong bond between the King and his beloved daughter-in-law.
Charlie Woods failed to advance in a U.S. Open local qualifying event Thursday, shooting a 9-over 81 at Legacy Golf & Tennis Club.
When it comes to cardiovascular fitness, you may tend to focus on activities that move you forward, such as walking, running and cycling.
American troops will be spending more time training in the Far North, the new commander of Norad says, a strategy that fits 'hand-in-glove' with Canada's renewed focus on Arctic defence.
Ashley Dickey and her mother rented part of the same Coquitlam duplex in three different decades under three different landlords.
A man who fell into a crevasse while leading a backcountry ski group deep in the Canadian Rockies has died.
During a special winner celebration near their hometown, Doug and Enid shared the story of how they discovered they were holding a Lotto Max ticket worth $70 million and how they kept this huge secret for so long.
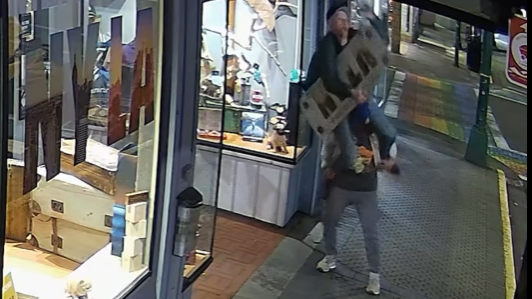
Mounties in Nanaimo, B.C., say two late-night revellers are lucky their allegedly drunken antics weren't reported to police after security cameras captured the men trying to steal a heavy sign from a downtown business.
A property tax bill is perplexing a small townhouse community in Fergus, Ont.
When identical twin sisters Kim and Michelle Krezonoski were invited to compete against some of the world’s most elite female runners at last week’s Boston Marathon, they were in disbelief.
The giant stone statues guarding the Lions Gate Bridge have been dressed in custom Vancouver Canucks jerseys as the NHL playoffs get underway.
A local Oilers fan is hoping to see his team cut through the postseason, so he can cut his hair.
A family from Laval, Que. is looking for answers... and their father's body. He died on vacation in Cuba and authorities sent someone else's body back to Canada.
A former educational assistant is calling attention to the rising violence in Alberta's classrooms.
The federal government says its plan to increase taxes on capital gains is aimed at wealthy Canadians to achieve “tax fairness.”
At 6'8" and 350 pounds, there is nothing typical about UBC offensive lineman Giovanni Manu, who was born in Tonga and went to high school in Pitt Meadows.