
B.C. tenants evicted for landlord's use after refusing large rent increase to take over neighbouring suite
Ashley Dickey and her mother rented part of the same Coquitlam duplex in three different decades under three different landlords.
An extensive study of thousands of COVID-19 patients in Ontario hospitals found links between the severity of their infections and the levels of common air pollutants they experience.
"This adds to existing evidence that air pollution is a silent killer," said Chen Chen, an environmental epidemiologist at the University of California and lead author of the study published in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
The study looked at more than 150,000 COVID-19 cases in Ontario patients in 2020. It broke out how many of those patients were admitted to hospital because of the disease, how many were transferred to intensive care units and how many died.
Researchers then turned to previously developed data that combined air monitoring records with other sources, such as satellite imagery, to model levels across Ontario of three common pollutants -- fine particles, nitrogen dioxide and ground-level ozone.
Nitrogen dioxide is emitted in engine exhaust, which then breaks down in the atmosphere into ozone. All three pollutants together create smog.
The scientists then combined the health and pollution data, using statistical methods to weed out the effects of more than 10 different "confounding factors," such as pre-existing conditions and economic status.
The researchers were able to show that more severe reactions to the virus were associated with higher levels of long-term exposure to air contaminants.
For every 25 per cent increase in fine particles a patient had been exposed to, the chance of being admitted to hospital after being infected with COVID-19 increased by six per cent and the odds of being admitted into an ICU increased nine per cent. The team found no links between death rates and particulate exposure.
The effects were smaller for nitrogen dioxide.
But for ground-level ozone, the study found correlations for every 25 per cent increase in exposure were much higher.
The chances of hospital admission increased 15 per cent. Intensive care admissions increased 30 per cent and death rates went up 18 per cent.
"Of those people who were already infected, we observed some of them who were exposed to higher air pollution levels prior to their infection have a higher probability of worse outcomes," Chen said.
The study builds on previous research that looked at immediate links between pollution levels and COVID-19 infections. Chen said that approach fails to capture what could be the long-term effects of air pollutants.
"We were looking at long-term pollution levels and their impact on COVID severity."
Chen cautioned the study doesn't establish that the three pollutants actually caused the worsening COVID-19 outcomes.
But it wouldn't be a surprise. Those contaminants are all known to irritate lungs and lung function, and COVID-19 is a pulmonary disease.
"We know this virus attacks our pulmonary system," she said. "It's possible that being exposed to more air pollution prior to infection makes you more susceptible."
Chen said the study opens the door to more detailed research on the variation in COVID-19 outcomes. What is the impact of age, for example, or economic status?
As well, the study doesn't look for the mechanism of how air pollution might work to worsen the disease.
"This research raises a lot of questions," said Chen.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published May 24, 2022.

Ashley Dickey and her mother rented part of the same Coquitlam duplex in three different decades under three different landlords.
A man who fell into a crevasse while leading a backcountry ski group deep in the Canadian Rockies has died.
A new survey by Dalhousie University's Agri-Food Analytics Lab asked Canadians about their food consumption habits amid rising prices.
MPP Sarah Jama was asked to leave the Legislative Assembly of Ontario by House Speaker Ted Arnott on Thursday for wearing a keffiyeh, a garment which has been banned at Queen’s Park.
Charlie Woods failed to advance in a U.S. Open local qualifying event Thursday, shooting a 9-over 81 at Legacy Golf & Tennis Club.
As Donald Trump was running for president in 2016, his old friend at the National Enquirer was scooping up potentially damaging stories about the candidate and paying out tens of thousands of dollars to keep them from the public eye.
After Prime Minister Justin Trudeau said the federal government would still send Canada Carbon Rebate cheques to Saskatchewan residents, despite Saskatchewan Premier Scott Moe's decision to stop collecting the carbon tax on natural gas or home heating, questions were raised about whether other provinces would follow suit. CTV News reached out across the country and here's what we found out.
A Montreal actress, who has previously detailed incidents she had with disgraced Hollywood producer Harvey Weinstein, says a New York Court of Appeals decision overturning his 2020 rape conviction is 'discouraging' but not surprising.
Caleb Williams is heading to the Windy City, aiming to become the franchise quarterback Chicago has sought for decades.
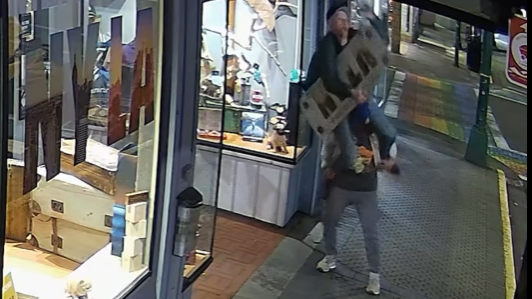
Mounties in Nanaimo, B.C., say two late-night revellers are lucky their allegedly drunken antics weren't reported to police after security cameras captured the men trying to steal a heavy sign from a downtown business.
A property tax bill is perplexing a small townhouse community in Fergus, Ont.
When identical twin sisters Kim and Michelle Krezonoski were invited to compete against some of the world’s most elite female runners at last week’s Boston Marathon, they were in disbelief.
The giant stone statues guarding the Lions Gate Bridge have been dressed in custom Vancouver Canucks jerseys as the NHL playoffs get underway.
A local Oilers fan is hoping to see his team cut through the postseason, so he can cut his hair.
A family from Laval, Que. is looking for answers... and their father's body. He died on vacation in Cuba and authorities sent someone else's body back to Canada.
A former educational assistant is calling attention to the rising violence in Alberta's classrooms.
The federal government says its plan to increase taxes on capital gains is aimed at wealthy Canadians to achieve “tax fairness.”
At 6'8" and 350 pounds, there is nothing typical about UBC offensive lineman Giovanni Manu, who was born in Tonga and went to high school in Pitt Meadows.