TORONTO -
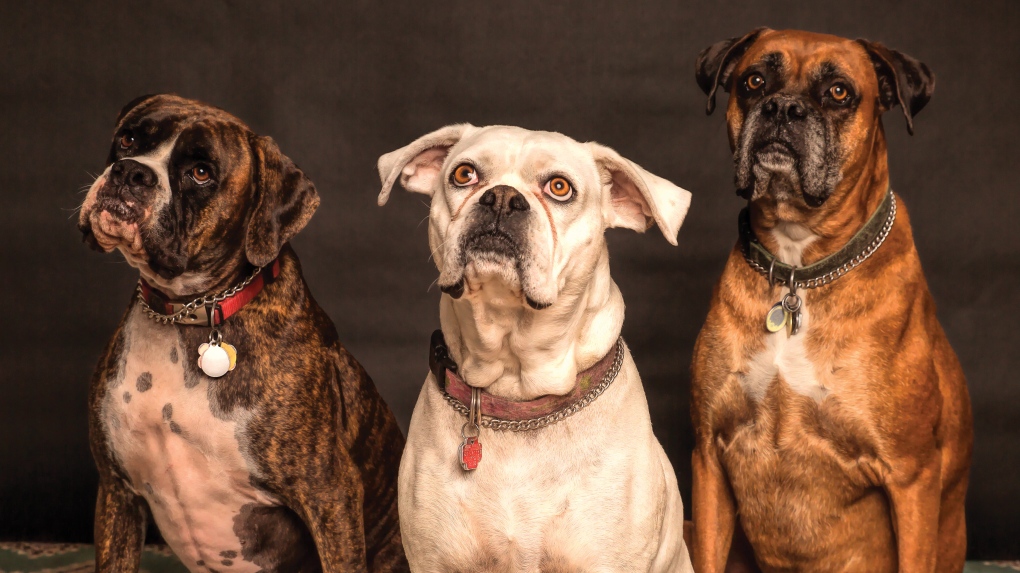
A new study has found raw dog food to be a major source of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which researchers say poses an international public health risk.
The research warns that "the trend for feeding dogs raw food may be fuelling the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria," with the bacteria in raw dog food "identical" to those found in hospital patients in several EU countries.
In the study, researchers out of the University of Porto in Portugal analyzed dog food from various supermarkets and pet shops for Enterococci, a type of drug-resistant bacteria that lives in the gut of humans and animals but can cause severe infections if found in other parts of the body.
They examined 55 samples of dog food from 25 brands, including wet, dry, semi-wet, raw frozen and treats, available in Europe and the United States. According to the study, the raw-frozen foods included duck, salmon, turkey, chicken, lamb, goose, beef and vegetables.
It is unclear if the dog foods studied are also sold in Canada.
In an email to CTVNews.ca on Tuesday, Freitas said the brands were not disclosed in the study as researchers would need a "more robust study" with a larger number of samples to "extract conclusions about differences in brands."
Of the foods studied, researchers reported that 30 samples (54 per cent) contained Enterococci and all of the raw food samples contained the drug-resistant bacteria.
By comparisons, only three of the non-raw samples contained Enterococci, according to researchers.
"The close contact of humans with dogs and the commercialization of the studied brands in different countries poses an international public health risk," Ana Freitas, a microbiologist and one of the study's authors, said in a press release.
The findings, published online in the International Journal of Food Microbiology, were presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) on Saturday.
The study reported that 40 per cent of the Enterococci found were resistant to antibiotics including erythromycin, tetracycline, quinupristin-dalfopristin, streptomycin, gentamicin, chloramphenicol, ampicillin and ciprofloxacin.
Researchers noted that there was also resistance to vancomycin and teicoplanin, and 23 per cent of the Enterococci were resistant to linezolid.
Linezolid is a "last-resort antibiotic" used on severe infections when other drugs have failed. It is considered a "critically important treatment" by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Using genetic sequencing, the researchers also found that some of the multi-drug resistant bacteria in the raw dog foods was similar to bacteria isolated from hospital patients in the United Kingdom, Germany and the Netherlands.
In another experiment, researchers transferred the antibiotic resistance genes from the bacteria found in dog foods to other bacteria, showing that this can occur in nature.
The researchers warn that the antibiotic-resistant bacteria found in dog foods could potentially spread to humans and may be an "overlooked driver" of antibiotic resistance globally.
The WHO classes antibiotic resistance as "one of the greatest public health threats facing humanity," with drug-resistant infections killing an estimated 700,000 people a year globally.
Experts say that figure is projected to rise to 10 million by 2050 if no action is taken.
To protect themselves, Freitas says, dog owners should always wash their hands with soap and water after handling pet food or cleaning up after their dog. In addition, the researchers are calling on the practices of pet food manufacturers to be assessed.
"European authorities must raise awareness about the potential health risks when feeding raw diets to pets and the manufacture of dog food, including ingredient selection and hygiene practices, must be reviewed," Freitas said in the release.