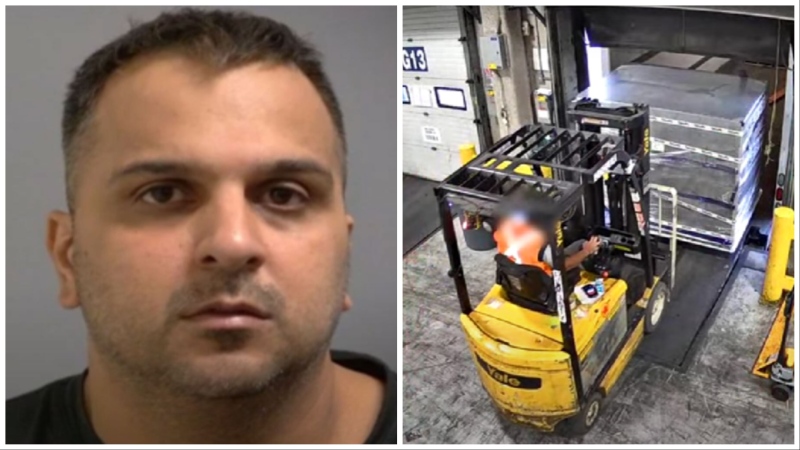

BREAKING Pearson gold heist suspect arrested after flying into Toronto from India
Another suspect is in custody in connection with the gold heist at Toronto Pearson International Airport last year, police say.
Throughout the pandemic, public health experts have tried numerous strategies to increase vaccine uptake and combat fears surrounding COVID-19 vaccines — but according to a new U.S. survey, having a personal connection to someone who caught COVID-19 may be a greater predictor of vaccine intake than any scientific strategy.
Researchers surveyed more than 1,000 Americans in 2021 regarding whether they had received at least one shot of the COVID-19 vaccine, and outlined their research in a study published in the peer-reviewed journal Vaccine in January.
Participants were asked if they had any family members or friends who had been sick with or died of COVID-19.
What the study found was that those who had witnessed a loved one battle COVID-19 or die of it were more likely to have received at least one shot of the COVID-19 vaccine compared to those who didn’t have any loved ones impacted by the disease.
“These findings should encourage people to share stories about their COVID-19 illness and bereavement experiences with their friends and family as well as through social media as it may motivate people to be vaccinated,” Irina Grafova, health economist at Rutgers School of Public Health and co-author of the study, said in a news release on Feb 3. “It also can help public health professionals design educational strategies to improve calls to action for vaccination.”
In December 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued an emergency authorization for the Pfizer-BioNTech and the Moderna COVID-19 vaccines. The 2021 survey sought to discover who had taken advantage of the chance to get the vaccine in those first few months of its release in the U.S. and who was more hesitant.
The survey was conducted online in April 2021 and included 1,193 respondents who were eligible for the vaccine at that time. Researchers used a research panel service called Qualtrics, which is a study participant recruitment website within the U.S. Respondents were not aware of the focus of the survey prior to taking it.
The survey allowed participants to select multiple options if they knew more than one person who had been impacted by COVID-19. It also asked participants if they fell into an “essential worker” category, such as health workers, grocery store personnel, postal workers, public transport workers or first responders, in order to determine whether their employment had an impact on their vaccine intake.
Out of the 1,193 respondents, 698 had received at least one vaccine dose, while 495 had not, meaning around 58.5 per cent of those who were eligible had received a dose.
However, those who had personal experience of someone they knew being struck with the virus were far more likely to have received at least one dose by the study period.
Around 73 per cent of those who knew someone who had died of COVID-19 and 72 per cent of those who knew someone who had recovered from COVID-19 had received at least one dose of the vaccine, the survey found.
The study demonstrates that sometimes, “the messenger matters more than the message,” Saurabh Kalra, a doctoral student at the Rutgers School of Public Health and lead author of the study, said in the release.
Hearing about the dangers of COVID-19 from a person you trust can be really important to surmounting hesitations or fears, she said, adding that the opposite is true as well.
“A corollary to this finding is that an influential public figure whom people admire and trust can adversely impact public health if they share misinformation such as the disease is harmless or the vaccines are harmful or unnecessary.”
Researchers noted that their results don’t indicate whether people received their dose before or after their loved one caught COVID-19, so it isn’t known what percentage may have been inspired directly by the experience of their loved one’s illness. But the correlation suggests that there is some connection, they say.
Paul Duberstein, chair and professor in the department of health behaviour, society and policy at Rutgers School of Public Health and co-author of the study, said in the release that there is often a large social element to our health choices, and that decision makers should be taking this into account when constructing vaccine campaigns.
“Most health behaviours, including exercise, smoking and drug use, are subject to peer influence, so it is not surprising that vaccine use is also socially patterned,” he said. “We need to stop acting like people rationally make vaccine decisions by themselves based on a careful weighting of the evidence.”
Those who fell under the umbrella of essential workers were also more likely to have received at least one dose of the vaccine, the study found.
On the flip side, those who had less income and less education were among the populations least likely to have received at least one dose of the vaccine within the first four months of the vaccine being available in the U.S., potentially highlighting populations that public health should be gearing vaccine information campaigns towards.
“A timely vaccination to all eligible individuals worldwide is our only hope to end this pandemic prior to the emergence of newer variants that may make the current vaccinations ineffective,” the study stated in its conclusions.

Another suspect is in custody in connection with the gold heist at Toronto Pearson International Airport last year, police say.
Hailey and Justin Bieber are going to be parents. The couple announced the news on Thursday on Instagram, both sharing a video that showcases Hailey Bieber's growing belly.
A family of fifth generation farmers from Ituna, Sask. are trying to find answers after discovering several strange objects lying on their land.
A Conservative government led by Pierre Poilievre would not legislate on, nor use the notwithstanding clause, on abortion, his office says, as anti-abortion protesters gather on Parliament Hill.
A southwestern Ontario woman has received an $8,400 bill from a hospital in Windsor, Ont., after she refused to put her mother in a nursing home she hated -- and she says she has no intention of paying it.
Studies have shown that ultraprocessed foods can have a detrimental impact on health. But 30 years of research show they don’t all have the same impact.
Miss Teen USA resigned Wednesday, sending further shock waves through the pageant community just days after Miss USA said she would relinquish her crown.
Ontario Provincial Police confirm one person has died after a single-vehicle rollover crash in Sharbot Lake, Ont. that seriously injured five others.
A grieving mother is speaking out after her 36-year-old son was shot and killed in North Preston, N.S., Wednesday night.

A Listowel, Ont. man, drafted by the Hamilton Tigercats last week, is also getting looks from the NFL, despite only playing 27 games of football in his life.
A small Ajax dessert shop that recently received a glowing review from celebrity food critic Keith Lee is being forced to move after a zoning complaint was made following the social media influencer’s visit last month.
The Canada Science and Technology Museum is inviting visitors to explore their poop. A new exhibition opens at the Ottawa museum on Friday called, 'Oh Crap! Rethinking human waste.'
The Regina Police Service says it is the first in Saskatchewan and possibly Canada to implement new technology in its detention facility that will offer real-time monitoring of detainees’ vital health metrics.
The stakes have been set for a bet between Vancouver and Edmonton's mayors on who will win Round 2 of the Stanley Cup playoffs.
A grieving mother is hosting a helmet drive in the hopes of protecting children on Manitoba First Nations from a similar tragedy that killed her daughter.
A chicken farmer near Mattawa made an 'eggstraordinary' find Friday morning when she discovered one of her hens laid an egg close to three times the size of an average large chicken egg.
A P.E.I. lighthouse and a New Brunswick river are being honoured in a Canada Post series.
An Ontario man says he paid more than $7,700 for a luxury villa he found on a popular travel website -- but the listing was fake.
 A Jackson-Hinds Comprehensive Health Center nurse loads a syringe with a Moderna COVID-19 booster vaccine at an inoculation station next to Jackson State University in Jackson, Miss., Friday, Nov. 18, 2022. (AP Photo/Rogelio V. Solis)
A Jackson-Hinds Comprehensive Health Center nurse loads a syringe with a Moderna COVID-19 booster vaccine at an inoculation station next to Jackson State University in Jackson, Miss., Friday, Nov. 18, 2022. (AP Photo/Rogelio V. Solis)