
'He's in our hearts': Family and friends still seek answers one year after Nathan Wise’s disappearance
It’s been a year since Nathan Wise went missing and his family is no closer to finding out what happened to him.
As artificial intelligence software and advanced computers revolutionize modern technology, some researchers see a future where computer programmers leap from silicon to organic molecules.
Scientists with Johns Hopkins University are investigating the possibility of “biocomputers” – programs modelled from organic molecules such as human DNA or proteins – unlocking new insights on human biology and advancing the processing power of future tech.
Much of these technological anticipations derive from something called “organoids,” which are lab-grown tissues resembling fully grown organs, sharing similar biological complexities to tissues comprised in kidneys, lungs and brain cells.
Organoids, which have become more prominent in labs over the last two decades, currently offer scientists a more ethical alternative to animal or human testing, mimicking basic functions of cells and advancing scientific understandings towards how those cells operate.
Most recently, scientists with Johns Hopkins have been assessing the nature of “brain organoids,” which are orbs the size of a pen dot that mirror the basic neural functions of learning and remembering in the human brain, according to a news release.
“This opens up research on how the human brain works,” Thomas Hartung, a professor of environmental health sciences at Johns Hopkins, said in the release, adding that deeper insights into human cognition can also serve as a roadmap for unlocking greater computing power in future technology.
“Computing and artificial intelligence have been driving the technology revolution but they are reaching a ceiling,” he said. “Biocomputing is an enormous effort of compacting computational power and increasing its efficiency to push past our current technological limits.”
Hartung and his team first began growing brain organoids in 2012 by using cells from human skin samples that they reprogrammed to multiply and mirror the functions of other cells. Each of these organoids consist of approximately 50,000 cells, and Hartung and his team envision building a futuristic computer that uses the organization of these cells as a basis for new forms of computer programming.
Despite the fact that computer calculations involving numbers and data are far superior to brains in terms of speed and volume, Hartung pointed out that humans are currently more efficient in arriving at complex logical decisions with substantially less processing power required.
For instance, our ability to tell the difference between a cat and a dog based on a quick glance requires much less processing power than a computer program would require, despite the fact that an advance computer would be able to provide way more information on each species than the average person.
Through using the complexity of brain organoids and training them with artificial intelligence, Hartung believes “biocomputers” can reach new computing speed, processing power, storage capabilities, and general data efficiency.
“Computers that run on this ‘biological hardware’ could in the next decade begin to alleviate energy consumption demands of supercomputing that are becoming increasingly unsustainable,” he said.
He added that it could be decades before an organoid-based computer would effectively function, but that the possibility remains as the field of organoid research expands.
Lena Smirnova, a Johns Hopkins assistant professor of environmental health and engineering, who is co-leading the investigation, added that such research could revolutionize drug testing research for neurodegeneration and neurodevelopmental disorders.
“The tools we are developing towards biological computing are the same tools that will allow us to understand changes in neuronal networks specific for autism, without having to use animals or to access patients,” she said in the news release. By advancing bio-computing, Smirnova believes researchers can “understand the underlying mechanisms of why patients have these cognition issues and impairments.”
Smirnova and Hartung further outlined their plans for assessing the future of organoid intelligence and bio-computing in the journal Frontiers in Science last month.

It’s been a year since Nathan Wise went missing and his family is no closer to finding out what happened to him.
Dozens of Ontarians are expressing frustration in the province’s health-care system after their family doctors either dropped them as patients or threatened to after they sought urgent care elsewhere.
An Ottawa pizzeria is being recognized as one of the top 20 deep-dish pizzas in the world.
Amazon's paid subscription service provides free delivery for online shopping across Canada except for remote locations, the company said in an email. While customers in Iqaluit qualify for the offer, all other communities in Nunavut are excluded.
The fire burning near Fort McMurray grew from 25 hectares to 5,500 hectares over the weekend.
Russia’s President Vladimir Putin began a Cabinet shakeup on Sunday, proposing the replacement of Sergei Shoigu as defence minister as he begins his fifth term in office.
Police are searching for a male suspect after a man was “slashed in neck” on Sunday morning in downtown Toronto and died.
There were some scary moments for several people on a northern Ontario highway caught on video Thursday after a chain reaction following a truck fire.
Health Canada announced various product recalls this week, including electric adapters, armchairs, cannabis edibles and vehicle components.

English, history, entertainment, math and geography: high school trivia teams could be quizzed on any of it when they compete at the Reach for the Top Nationals in Ottawa in June.
An Ottawa pizzeria is being recognized as one of the top 20 deep-dish pizzas in the world.
A family of fifth generation farmers from Ituna, Sask. are trying to find answers after discovering several strange objects lying on their land.
A Listowel, Ont. man, drafted by the Hamilton Tigercats last week, is also getting looks from the NFL, despite only playing 27 games of football in his life.
The threat of zebra mussels has prompted the federal government to temporarily ban watercraft from a Manitoba lake popular with tourists.
A small Ajax dessert shop that recently received a glowing review from celebrity food critic Keith Lee is being forced to move after a zoning complaint was made following the social media influencer’s visit last month.
The Canada Science and Technology Museum is inviting visitors to explore their poop. A new exhibition opens at the Ottawa museum on Friday called, 'Oh Crap! Rethinking human waste.'
The Regina Police Service says it is the first in Saskatchewan and possibly Canada to implement new technology in its detention facility that will offer real-time monitoring of detainees’ vital health metrics.
Just as she had feared, a restaurant owner from eastern Quebec who visited Montreal had her SUV stolen, but says it was all thanks to the kindness of strangers on the internet — not the police — that she got it back.
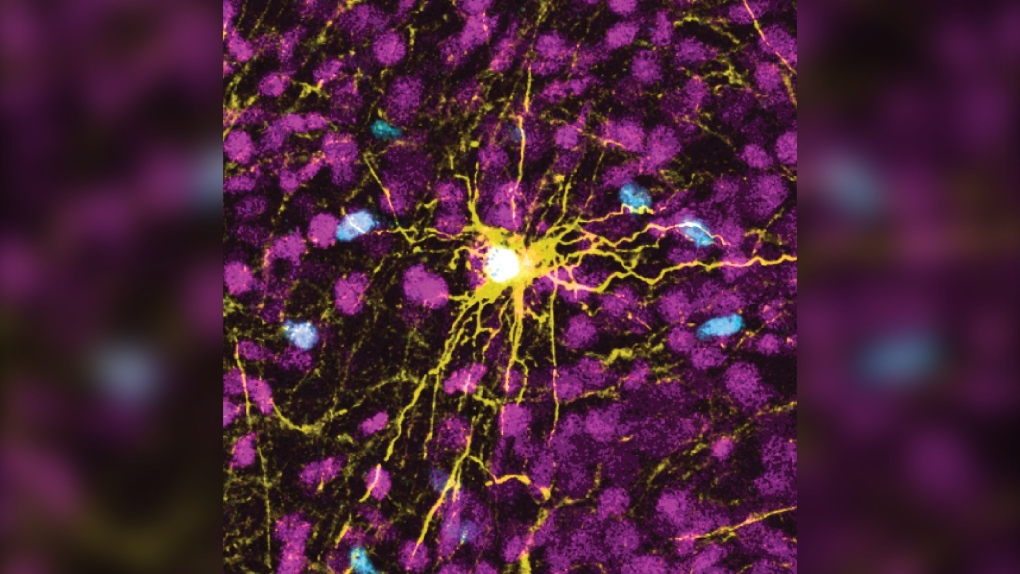 This microscope image provided by Pasca Lab/Stanford Medicine shows a human astrocyte cell, center in yellow, and human glial cells (scattered in blue) inside the brain of a rat. (Pasca Lab/Stanford Medicine via AP)
This microscope image provided by Pasca Lab/Stanford Medicine shows a human astrocyte cell, center in yellow, and human glial cells (scattered in blue) inside the brain of a rat. (Pasca Lab/Stanford Medicine via AP)