LONDON -
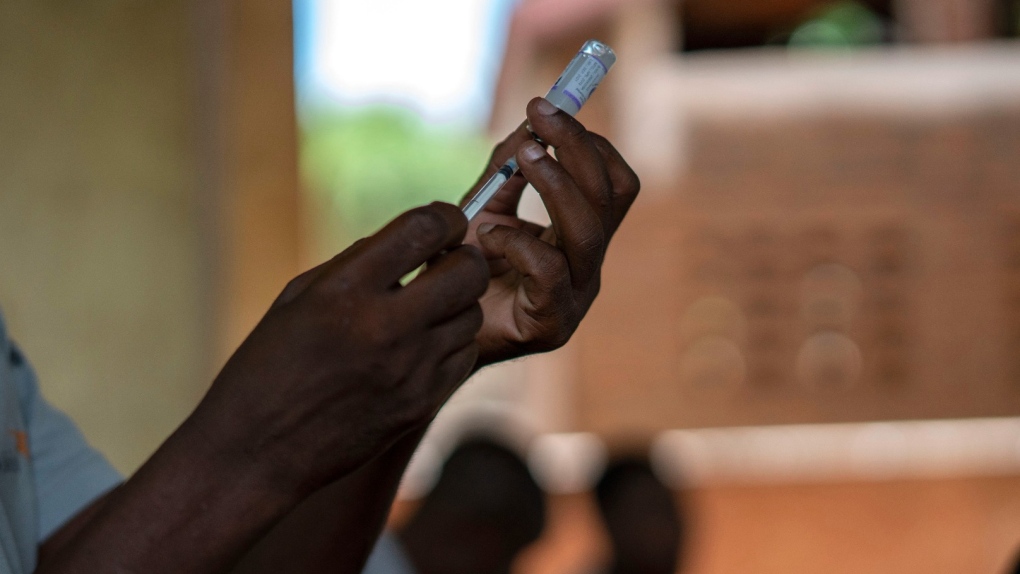
The World Health Organization authorized a second malaria vaccine on Monday, a decision that could offer countries a cheaper and a more readily available option than the world's first shot against the parasitic disease.
WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said the UN health agency was approving the new malaria vaccine based on the advice of two expert groups, recommending its use in children at risk of the disease.
"As a malaria researcher, I used to dream of the day we would have a safe and effective vaccine against malaria. Now we have two," Tedros said.
Oxford University developed the new three-dose vaccine with help from the Serum Institute of India. Research suggests it is more than 75 per cent effective and that protection is maintained for at least another year with a booster. Tedros said the shot would cost about $2 to $4 and could be available in some countries next year if funders agree to buy it.
Earlier this year, regulatory authorities in Ghana and Burkina Faso approved the vaccine.
"This is one more tool we will now have, but it's not going to replace bed nets and spraying insecticides," said John Johnson with Doctors Without Borders. "This is not the vaccine that's going to stop malaria."
Johnson was not part of the WHO expert group that gave the Oxford vaccine the green light.
In 2021, WHO endorsed the first malaria vaccine in what it described as a "historic" effort to end the devastating toll the mosquito-transmitted disease has on Africa, home to most of the world's estimated 200 million cases and 400,000 deaths.
But that vaccine, known as Mosquirix and made by GSK, is only about 30 per cent effective, requires four doses and protection fades within months. WHO experts, however, said the data to date on the GSK and Oxford-developed vaccines does not show which one is more effective.
The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, one of the GSK vaccine's biggest backers, stepped back last year from financially supporting Mosquirix's rollout directly, saying it was less effective than officials would like and that funding would be better used elsewhere. The foundation said it has continued helping with the vaccine rollout by supporting Gavi, a global vaccines alliance that is buying the GSK shots for distribution in poorer countries.
"The big difference with these two vaccines is access," Johnson said, noting that only about a dozen countries are scheduled to get limited quantities of the GSK vaccine in the next few years.
GSK has said it can only produce about 15 million doses a year. The Serum Institute has said it could make up to 200 million doses of the Oxford vaccine a year.
 A baby from the Malawi village of Tomali is injected with the world's first vaccine against malaria in a pilot program, on Dec. 11, 2019. (AP Photo/Jerome Delay, File)Alister Craig, an emeritus professor at the Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, said he would recommend countries trying to get the GSK vaccine switch to the Oxford vaccine instead.
A baby from the Malawi village of Tomali is injected with the world's first vaccine against malaria in a pilot program, on Dec. 11, 2019. (AP Photo/Jerome Delay, File)Alister Craig, an emeritus professor at the Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, said he would recommend countries trying to get the GSK vaccine switch to the Oxford vaccine instead.
If the new vaccine is rolled out widely across Africa, it could dramatically reduce the amount of severe illness and deaths caused by malaria in a few years, Craig said.
Neither of the malaria vaccines stop transmission so immunization campaigns alone won't be enough to stop epidemics. Efforts to curb the disease are also being complicated by increasing reports of resistance to the main drugs used to treat malaria and the spread of invasive mosquito species.
"You would be foolish to think that this vaccine is going to be the end of the malaria story," Craig said.
In a separate decision, WHO's expert group also authorized the dengue vaccine made by Takeda, which was previously approved by the European Union drug regulator.
There is no specific treatment for dengue, common in tropical Latin American and Asian countries. While most infections are mild, severe cases of the mosquito-spread disease can lead to internal bleeding, organ damage and death.
WHO's expert groups advised that the Takeda dengue vaccine be used in children aged six to 16 in countries with a high prevalence of the disease.
Previous studies have showed Takeda's vaccine was about 84 per cent effective in preventing people from being hospitalized with dengue and about 61 per cent effective in stopping symptoms four years after getting immunized.
Nearly 1,000 people have been killed by dengue this year in an ongoing epidemic in Bangladesh, the country's worst outbreak of the disease.
------
Associated Press writer Jamey Keaten in Geneva contributed to this report.
------
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute's Science and Educational Media Group. The AP is solely responsible for all content.