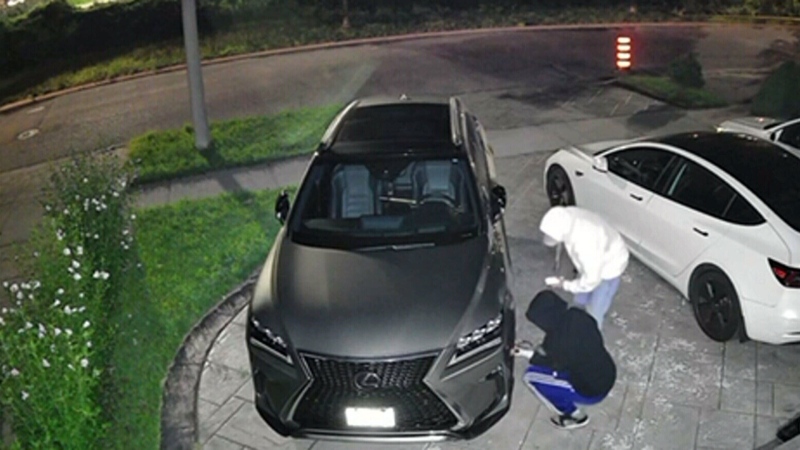
A new study suggests that many people taking herbal supplements such as ginseng or green tea are unaware that the so-called "natural" remedies can interact with their prescription medication, leading to potentially dangerous complications.
The study, published Wednesday in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, reviewed dozens of case reports of people who had experienced "adverse drug reactions" when herbal supplements were taken along with medication.
The majority of the patients were taking blood thinners such as warfarin, or statins to treat high cholesterol. They reported significant interactions from herbal products containing cranberry juice, goji juice, green tea, chamomile, flaxseed, ginseng, and St. John's wort.
The analysis included 49 case reports of adverse reactions and two studies involving 15 more drug reactions. The reports included patients on warfarin, chemotherapy drugs, or immunosuppressant medication following an organ transplant.
In some cases, the herbal remedies blocked the effect of the prescription medications, causing patients to respond poorly to the drug. In other cases, the patients had to be hospitalized because the herbal products led to toxic buildups of needed medications.
Several herbal medicines, such as ginseng, sage and flaxseed are known to interfere with a key liver enzyme needed to regulate the blood thinner warfarin, leading to either bleeding episodes or blood clotting.
Some of the cases involved organ transplant patients on anti-rejection drugs who experienced severe kidney problems after taking turmeric or chamomile tea.
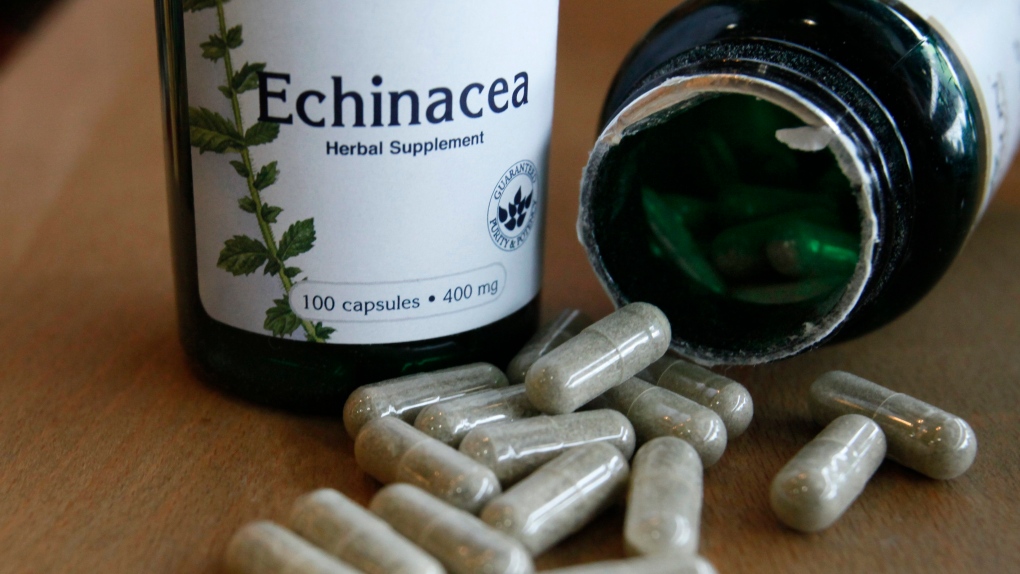
Other case reports described cancer patients taking chemotherapy who experienced liver problems and hepatitis after drinking ginseng-infused energy drinks, or herbal medicines with echinacea or chokeberry juice.
The researchers say more needs to be done to increase patient awareness of the potential interaction between herbal products and prescribed medicines, so patients understand the potential risks.
As well, the authors write, studies on herbal medicines "must be publicized to alert both clinicians and patients about the need to avoid co-usage of certain herbal medicines with specific prescribed medications."