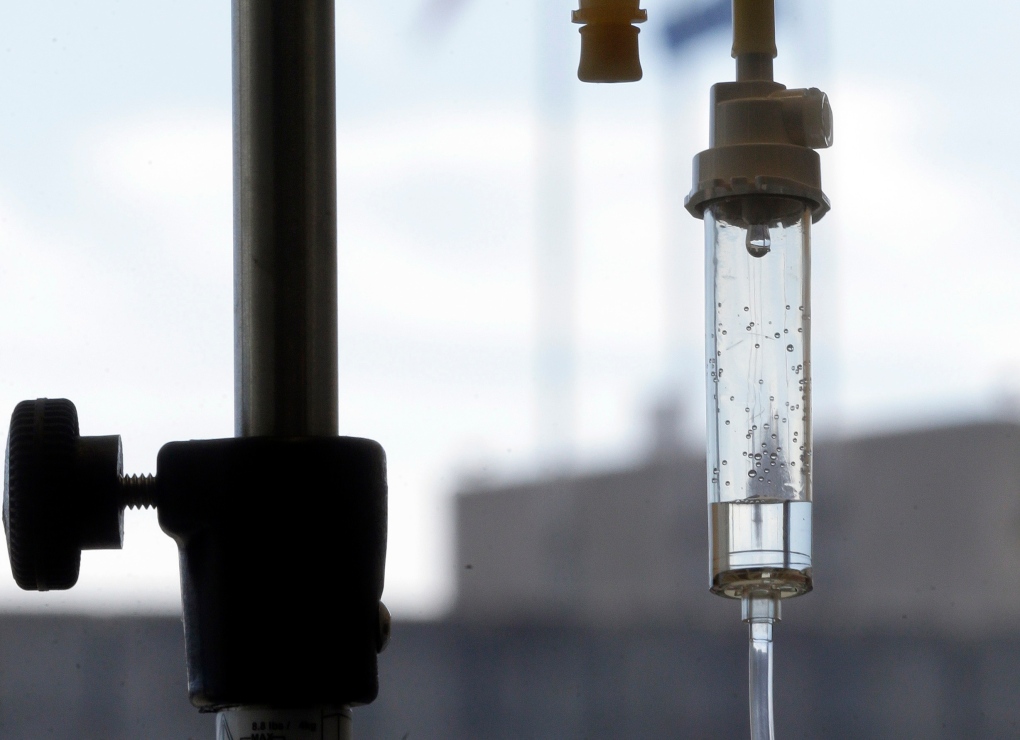
New research calls into question what's in those IV bags that nearly every hospitalized patient gets. Two large studies found that using a different intravenous fluid instead of the usual saline greatly reduced a patient's risk of death or kidney damage.
Each year, millions of people get an IV to prevent dehydration or to receive medicines.
Saline, which is salt water, is the most widely used fluid in the U.S. But the studies found safety improved when balanced fluids were used. They contain potassium and other things to make them more like natural plasma.
Switching could save tens of thousands of lives a year, doctors estimate.
Results were discussed Tuesday at a conference and published by the New England Journal of Medicine.