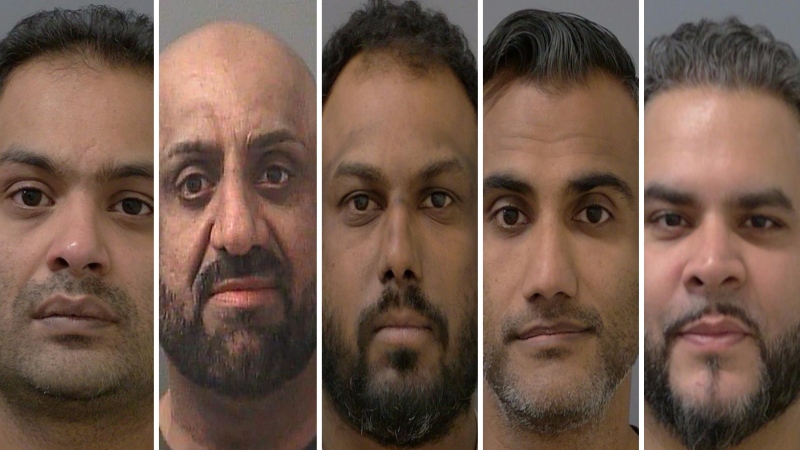
MINNEAPOLIS -- A Minnesota judge has dismissed a third-degree murder charge filed against the former Minneapolis police officer who pressed his knee against George Floyd's neck, saying there was not enough probable cause for that count to proceed to trial. The more serious second-degree murder charge against Derek Chauvin remains.
Hennepin County District Judge Peter Cahill's ruling, dated Wednesday and made public Thursday, found probable cause for Chauvin to be tried on one count of unintentional second-degree murder and one count of second-degree manslaughter. Cahill also found probable cause to move forward with the aiding and abetting counts against three other former officers, Thomas Lane, J. Kueng and Tou Thao.
"In this court's view, with one exception, the State has met its burden of showing probable cause that warrants proceeding to trial against each of these Defendants on each of the criminal charges the State has filed against them," Cahill wrote. He said a jury will decide whether they are guilty.
Floyd, a Black man in handcuffs, died May 25 after Chauvin, who is white, pressed his knee against Floyd's neck as he said he couldn't breathe. Floyd's death sparked protests in Minneapolis and beyond, and led to a nationwide reckoning on race. All four officers were fired. They are scheduled to stand trial in March.
In light of Cahill's ruling, Gov. Tim Walz activated the Minnesota National Guard in anticipation of protests. Protesters demonstrated in the streets after Chauvin was released on bail earlier this month, resulting in dozens of arrests.
On the second-degree murder charge, prosecutors presented probable cause to show Chauvin's actions were a "substantial causal factor" in Floyd's death, and that he was committing or attempting to commit another felony at the time, in this case, assault, Cahill wrote.
He said prosecutors do not need to show Chauvin's actions were the sole cause of Floyd's death, and the facts offered by prosecutors so far are enough to present to a jury, which will determine Floyd's cause of death. He also said Chauvin's decision to continue kneeling on Floyd's neck after he went silent and motionless, and to ignore cries from bystanders, "is strong evidence of Chauvin's intent to inflict bodily harm."
To prove a third-degree murder charge, prosecutors must show that Chauvin's intentional conduct was "eminently dangerous to others" and not specifically directed at the person who died, Cahill said.
"This is not an appropriate case for a third-degree murder charge," he said.
While former Minneapolis police officer Mohamed Noor was convicted of third-degree murder in the 2017 killing of Justine Ruszczyk Damond, Cahill said the cases are "factually distinguishable." Noor fired a gun outside his squad car window, potentially endangering a nearby bicyclist, residents, possible bystanders, his partner, or others.
In this case, Cahill said, "nothing about the manner in which Chauvin pressed his knee down on Floyd's neck for nine-plus minutes while Kueng and Lane were also kneeling on Floyd's back and legs was eminently dangerous to anyone other than Floyd. And, nothing about that conduct can be said to have been done in heedless disregard for whether anyone other than Floyd, the person who was specifically the target and focus of Chauvin's actions."
Attorney Ben Crump said in a statement that Floyd's family is grateful that most of the counts were preserved, including the more serious second-degree murder count, "for which we expect a conviction, based on the clear and evident use of excessive force that we all saw on video."
Nicole Kettwick, a criminal defence attorney who is not associated with this case, said the dismissal of the third-degree murder count is not surprising and that the elements of the charge were not a good fit based on the facts currently known.
Cahill also found probable cause for the aiding and abetting charges to proceed against Lane, Kueng and Thao, saying they could be found criminally liable if prosecutors can prove they intentionally aided or conspired with Chauvin, and that they knew Chauvin was committing a crime at the time. He said prosecutors also must show that their presence or actions allowed the crime to continue.
Lane and Kueng heard Floyd say he couldn't breathe, knew Chauvin was kneeling on Floyd's neck, and heard the cries of the crowd, yet they continued to restrain Floyd by his legs and back, Cahill said. The fact that Lane asked if Floyd should be rolled to a recovery position shows that Lane knew "the consequences of keeping Floyd pinned face-down to the ground" but elected to "stay the course," Cahill said.
Lane never tried to extract himself from the situation or assertively tell Chauvin to stop, he said. Even if the initial restraint of Floyd was justified, that doesn't grant the defendants "carte blanche" to continue to restrain him without considering the changing circumstances, the judge said.
Lane and Kueng's rookie status is irrelevant, he said: "There is no free pass under state law for rookies who choose to disregard their training at the suggestion of a senior officer."
Cahill said Thao's position is somewhat different because he never physically restrained Floyd. But Thao could see and hear what was happening, and his actions to keep the crowd from intervening allowed the restraint of Floyd to continue.
Correction:
This story has been corrected to show the name of one of the officers charged in Floyd's death is J. Kueng, not J. Jueng.