
American millionaire Jonathan Lehrer denied bail after being charged with killing Canadian couple
American millionaire Jonathan Lehrer, one of two men charged in the killings of a Canadian couple in Dominica, has been denied bail.
Stonehenge's purpose has long been a mystery, with some researchers proposing that it may have been an ancient solar calendar. But now, new analysis suggests the calendar theory is unsubstantiated.
In a paper published last Thursday in the journal Antiquity, archeo-astronomers Giulio Magli and Juan Antonio Belmonte offered a rebuttal to an Antiquity paper published last year, which suggested Stonehenge's massive sandstone blocks known as "sarsens" corresponded to a calendar keeping track of a year lasting 365.25 days.
The 2022 paper argued that the sarsen stones corresponded to 12 months, each consisting of 30 days that were divided into three 10-day “weeks.” According to the paper, Stonehenge’s sarsens were added during the same phase of construction and were sourced from the same area and remained in the same position – suggesting they were meant to work as a single unit.
But Magli and Belmonte say the number 12 isn't recognizable anywhere in the monument, and that these theories amounted to "numerology," which refers to pseudoscientific interpretations of how numbers shape the world.
"The aim of the present letter is to show that this idea is unsubstantiated, being based as it is on a series of forced interpretations, numerology, and unsupported analogies with other cultures," Magli and Belmonte wrote.
Stonehenge does align with the sun on both the winter and summer solstices, suggesting that there was a "clear, symbolic interest of the builders to the solar cycle," the authors write.
"However, this is, of course, very far from saying that the monument was used as a giant calendrical device," they added.
The 2022 paper suggested the Neolithic builders of Stonehenge took inspiration from the ancient Egyptian calendar, which was also a solar calendar. But the Egyptian calendar only had 365 days in a year and had no leap years, meaning it would eventually go out of sync with the seasons.
Leap years only came into fruition after the adoption of the Julian calendar under the Roman Empire. According to the 2022 paper, the builders of Stonehenge not only learned about the Egyptian calendar, but improved upon that calendar 2,600 years before the Romans did --- a claim that is without any archeological proof, according to Magli and Belmonte.
On top of this, Magli and Belmonte say archeological evidence suggests most Neolithic societies, with the exception of the Egyptians and the Mayans, would've used lunar calendars. Having a solar calendar properly aligned with the seasons would've required a device with precision, such as a sundial, but the authors emphatically write, "Stonehenge is, evidently, not such a device!"
"We believe that matters such as ancient calendars, alignments and cultural astronomy should be reserved to specialists, to experienced people who have trained in the adequate dominion on the subject, and not left to enthusiasts, even if those same enthusiasts are renowned and knowledgeable specialists in their own field," they said.
With files from former CTVNews.ca writer Christy Somos

American millionaire Jonathan Lehrer, one of two men charged in the killings of a Canadian couple in Dominica, has been denied bail.
Cabinet minister Dominic LeBlanc says he plans to run in the next election as a candidate under Prime Minister Justin Trudeau's leadership, amid questions about his rumoured interest in succeeding his longtime friend for the top job.
A male columnist has apologized for a cringeworthy moment during former University of Iowa superstar and college basketball’s highest scorer Caitlin Clark’s first news conference as an Indiana Fever player.
The United States has vetoed a widely backed UN resolution that would have paved the way for full United Nations membership for the state of Palestine.
A group of suspects that allegedly defrauded seniors across Ontario and other parts of Canada using a so-called emergency grandparent scam appear to have ties to 'Italian traditional organized crime,' according to an investigator involved in the OPP-led probe.
Health Canada will change its longstanding policy restricting gay and bisexual men from donating to sperm banks in Canada, CTV News has learned. The federal health agency has adopted a revised directive removing the ban on gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men, effective May 8.
Prince Harry, the son of King Charles III and fifth in line to the British throne, has formally confirmed he is now a U.S. resident.
Kevin the cat has been reunited with his family after enduring a harrowing three-day ordeal while lost at Toronto Pearson International Airport earlier this week.
Technology from the 19th century has been brought out of retirement at a Newfoundland gardening store, as staff look for all the help they can get to fill orders during a busy season.
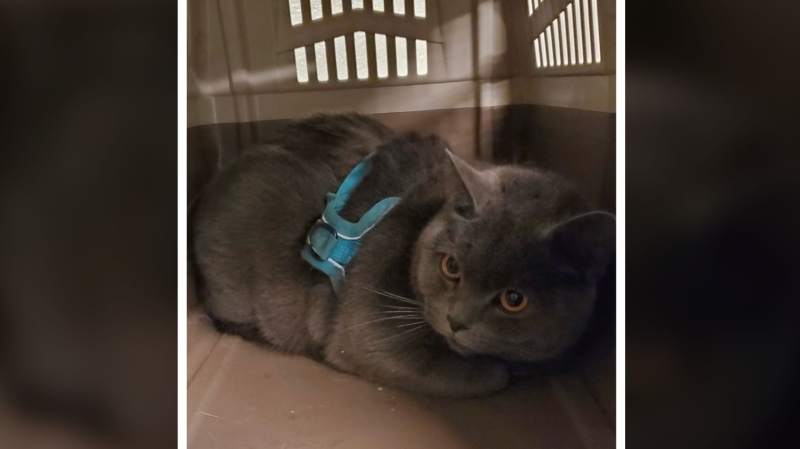
Kevin the cat has been reunited with his family after enduring a harrowing three-day ordeal while lost at Toronto Pearson International Airport earlier this week.
Molly Knight, a grade four student in Nova Scotia, noticed her school library did not have many books on female athletes, so she started her own book drive in hopes of changing that.
Almost 7,000 bars of pure gold were stolen from Pearson International Airport exactly one year ago during an elaborate heist, but so far only a tiny fraction of that stolen loot has been found.
When Les Robertson was walking home from the gym in North Vancouver's Lower Lonsdale neighbourhood three weeks ago, he did a double take. Standing near a burrow it had dug in a vacant lot near East 1st Street and St. Georges Avenue was a yellow-bellied marmot.
A moulting seal who was relocated after drawing daily crowds of onlookers in Greater Victoria has made a surprise return, after what officials described as an 'astonishing' six-day journey.
Just steps from Parliament Hill is a barber shop that for the last 100 years has catered to everyone from prime ministers to tourists.
A high score on a Foo Fighters pinball machine has Edmonton player Dave Formenti on a high.
A compound used to treat sour gas that's been linked to fertility issues in cattle has been found throughout groundwater in the Prairies, according to a new study.
While many people choose to keep their medical appointments private, four longtime friends decided to undergo vasectomies as a group in B.C.'s Lower Mainland.
 In this Tuesday, Dec. 17, 2013 file photo, visitors take photographs of the world heritage site of Stonehenge, in Wiltshire, England. (AP Photo/Alastair Grant, File)
In this Tuesday, Dec. 17, 2013 file photo, visitors take photographs of the world heritage site of Stonehenge, in Wiltshire, England. (AP Photo/Alastair Grant, File)