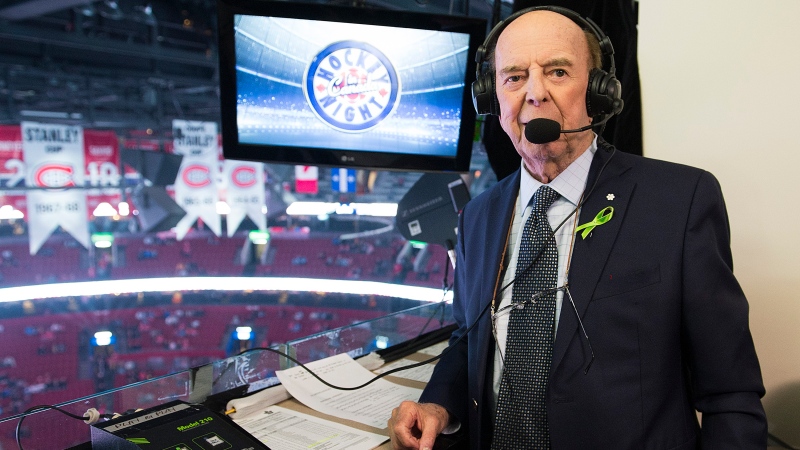

BREAKING Bob Cole, veteran CBC broadcaster and former voice of 'Hockey Night in Canada,' dead at 90
Bob Cole, legendary CBC broadcaster and former voice of Hockey Night in Canada, has died. He was 90.
An ancient human cousin may have buried its dead and carved symbols into cave walls, surprising findings for a creature with a small brain.
Fossil remains of the species -- named Homo naledi -- were uncovered in underground caves in South Africa a decade ago. Now, researchers say they've found evidence that the species was capable of complex behaviour that so far has only been seen in those with bigger brains.
"We are facing a remarkable discovery here" for a species with brains one-third the size of humans, said anthropologist Lee Berger, who led the research funded by the National Geographic Society, where he now works.
Berger and colleagues describe their findings in studies posted online Monday. The research has not been peer-reviewed yet and some outside scientists think more evidence is needed to challenge what we know about how humans evolved their complex thinking.
"There's still a lot to uncover," said Rick Potts, director of the Smithsonian's Human Origins Program who was not involved in the research.
H. naledi is a pretty new addition to the family tree of hominins, which includes our direct ancestors and other extinct relatives who walked on two legs. Berger and his team announced the species in 2015, after a tip from local spelunkers led them to the Rising Star cave system near Johannesburg where they uncovered fossils from at least 15 individuals who lived around 300,000 years ago.
These creatures had some traits in common with modern humans, like legs made for walking upright and hands that could work with objects, said University of Wisconsin-Madison anthropologist John Hawks, a member of the research team. But other features looked more ancient, including their small brains.
In recent years, team members have ventured back into the caves, a tricky descent through tight underground spaces. What's down there shows the species in a new light, they reported.
One of the new studies describes what researchers say were intentional burial sites. The team uncovered fossil remains of adults and children in shallow holes in the ground, their bodies in a fetal position.
Another study describes a series of marks carved into the cave walls, including geometric patterns and cross-hatched lines.
"This is something that takes a lot of time and effort to do," said Berger, who led the initial research while at the University of the Witwatersrand in Johannesburg.
All of this behaviour would be surprising for a creature whose brain was closer in size to an ape's than a human's, experts said.
Decades ago, we thought Homo sapiens were the only ones who could figure out how to use fire, bury their dead or create art, said Chris Stringer, a human evolution expert at London's Natural History Museum who was not involved in the research.
Since then, we've learned that other groups like Neanderthals also lived complex lives. But those species still had big brains -- unlike H. naledi, whose burials would raise further questions about human evolution, Stringer said.
Scientists haven't yet been able to identify how old the engravings are. So Potts said the current evidence can't say for sure whether H. naledi was truly the one to create the symbols, or if some other creature -- maybe even H. sapiens -- made its way down there at some point.
For study author Agustin Fuentes, an anthropologist at Princeton University, the H. naledi evidence takes the focus off brain size.
"Big brains are still important," Fuentes said. "They just don't explain what we thought they explained."
------
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute's Science and Educational Media Group. The AP is solely responsible for all content.

Bob Cole, legendary CBC broadcaster and former voice of Hockey Night in Canada, has died. He was 90.
New York's highest court on Thursday overturned Harvey Weinstein's 2020 rape conviction, reversing a landmark ruling of the #MeToo era in determining the trial judge improperly allowed women to testify about allegations against the ex-movie mogul that weren't part of the case.
Honda is set to build an electric vehicle battery plant next to its Alliston, Ont., assembly plant, which it is retooling to produce fully electric vehicles, all part of a $15-billion project that is expected to include up to $5 billion in public money.
MPP Sarah Jama was asked to leave the Legislative Assembly of Ontario by House Speaker Ted Arnott on Thursday for wearing a keffiyeh, a garment that is banned at Queen’s Park.
Researchers are working to better understand if some Canadian military veterans may be suffering from Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy, also known as CTE -- a disorder previously found in the brains of professional football and hockey players after their death.
Residents of John D'Or Prairie, a community on the Little Red River Cree Nation in northern Alberta, were told to take shelter Thursday morning during a police operation.
During a special winner celebration near their hometown, Doug and Enid shared the story of how they discovered they were holding a Lotto Max ticket worth $70 million and how they kept this huge secret for so long.
A West Virginia father is getting some sense of closure after authorities found the remains of his young daughter and her mother following a deathbed confession from the man believed to have fatally shot them nearly two decades ago.
The first cargo ship passed through a newly opened deep-water channel in Baltimore on Thursday after being stuck in the harbor since the Francis Scott Key Bridge collapsed four weeks ago, halting most maritime traffic through the city's port.
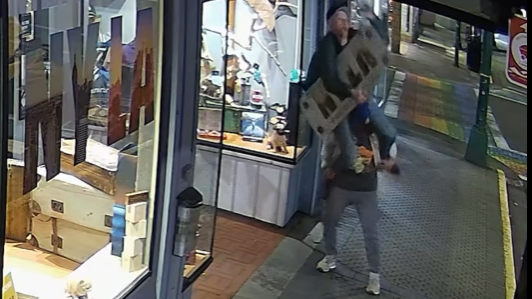
Mounties in Nanaimo, B.C., say two late-night revellers are lucky their allegedly drunken antics weren't reported to police after security cameras captured the men trying to steal a heavy sign from a downtown business.
A property tax bill is perplexing a small townhouse community in Fergus, Ont.
When identical twin sisters Kim and Michelle Krezonoski were invited to compete against some of the world’s most elite female runners at last week’s Boston Marathon, they were in disbelief.
The giant stone statues guarding the Lions Gate Bridge have been dressed in custom Vancouver Canucks jerseys as the NHL playoffs get underway.
A local Oilers fan is hoping to see his team cut through the postseason, so he can cut his hair.
A family from Laval, Que. is looking for answers... and their father's body. He died on vacation in Cuba and authorities sent someone else's body back to Canada.
A former educational assistant is calling attention to the rising violence in Alberta's classrooms.
The federal government says its plan to increase taxes on capital gains is aimed at wealthy Canadians to achieve “tax fairness.”
At 6'8" and 350 pounds, there is nothing typical about UBC offensive lineman Giovanni Manu, who was born in Tonga and went to high school in Pitt Meadows.
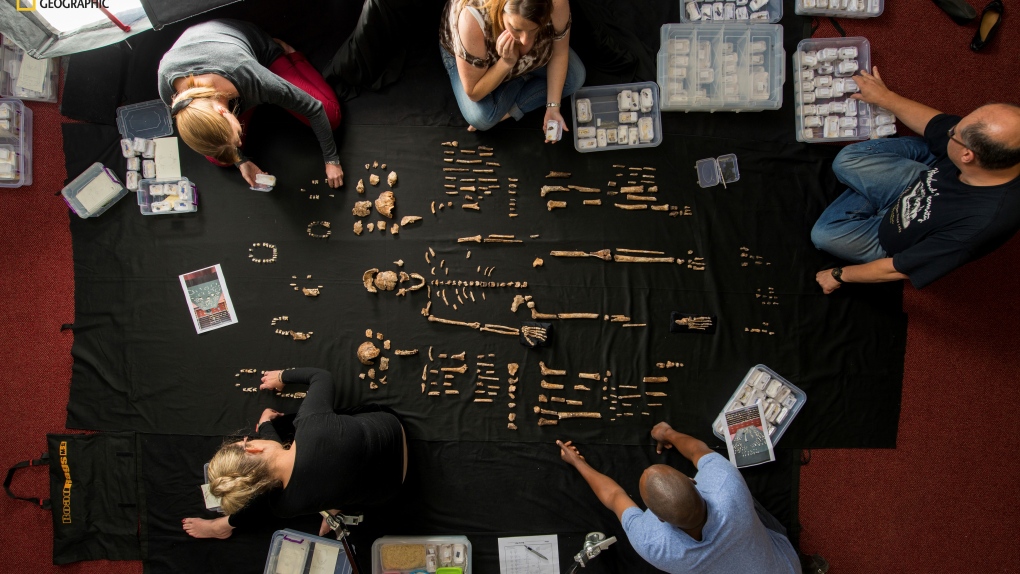 In this photo provided by National Geographic, researchers lay out fossils of Homo naledi at the University of the Witwatersrand's Evolutionary Studies Institute in Johannesburg, South Africa in 2014. (Robert Clark/National Geographic via AP)
In this photo provided by National Geographic, researchers lay out fossils of Homo naledi at the University of the Witwatersrand's Evolutionary Studies Institute in Johannesburg, South Africa in 2014. (Robert Clark/National Geographic via AP)