White-tailed deer may be a reservoir for COVID-19 variants of concern that no longer circulate among people, including Alpha, Delta and Gamma, according to new research out of Cornell University.
The authors say the research raises questions about whether deer could re-introduce nearly extinct variants back into the human population.
In a study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on Jan. 31, scientists from Cornell's College of Veterinary Medicine detailed how evidence of widespread infection with variants of concern (VOC) was found in deer across New York State in 2020 and 2021.
They wrote that the virus likely spread to deer from humans at some point before going "nearly extinct" in the human population.
While the pathways for transmission of the virus from humans to white-tailed deer are still somewhat of a mystery, the researchers said human activities such as feeding deer or baiting them for hunting could provide the opportunity for transmission.
"Findings indicate that white-tailed deer – the most abundant large mammal in North America – may serve as a reservoir for variant SARS-CoV-2 strains that no longer circulate in the human population," the authors wrote, adding that the findings "raised concerns about the role of white-tailed deer in the epidemiology and ecology of the virus."
During the September-to-December hunting seasons in 2020 and 2021, researchers collected 5,462 lymph node samples from free-ranging hunter-harvested white-tailed deer. Of those, 2,700 were from 2020 and 2,762 were from 2021.
Using PCR tests, they found SARS-CoV-2 RNA in 17 samples from 2020 and in 583 samples from 2021. They identified multiple COVID-19 "hotspots" throughout New York, and found the virus had spread significantly between the two hunting seasons, infecting deer in 10 counties in 2020 and 48 counties in 2021. The tests revealed white-tailed deer had been infected with SARS-CoV-2 in nine of the ten geographic regions of the state.
They also revealed that the viral RNA sequences in the deer were dramatically different from those in humans, suggesting the virus had adapted, or mutated, in its new hosts.
"Our analysis suggests the occurrence of multiple spillover events (human to deer) of the Alpha and Delta lineages with subsequent deer-to-deer transmission and adaptation of the virus," the authors wrote.
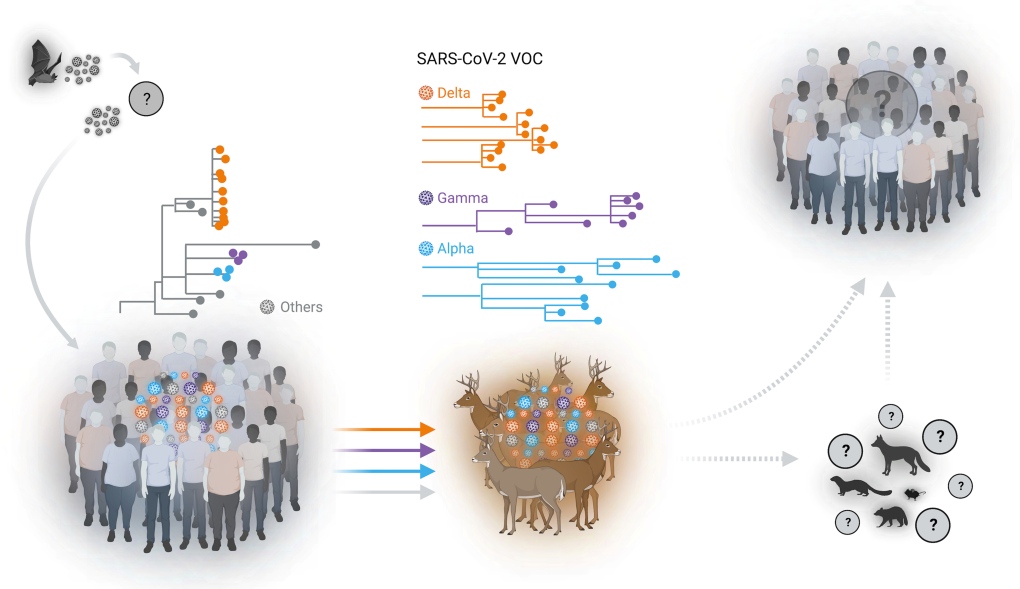 A graphic provided by the study authors shows several several SARS-CoV2 spillover events, including the hypothetical spillover of the virus from white-tailed deer to other animal species and back to humans. (Mathias Martins et al/Cornell University)
A graphic provided by the study authors shows several several SARS-CoV2 spillover events, including the hypothetical spillover of the virus from white-tailed deer to other animal species and back to humans. (Mathias Martins et al/Cornell University)
"The impact of such mutations on the virus' ability to transmit between white-tailed deer or from white-tailed deer to humans is still unknown and should be investigated in the future as it may shed light on mechanisms that affect the risk of deer-to-human transmission of the virus."
Scientists already know SARS-CoV-2 – the virus that causes COVID-19 – can spread among animals.
Most of the first known human infections were linked to the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in Wuhan, China, where several live wild animal species were sold. Additionally, genome sequencing has revealed a high similarity between SARS-CoV-2 and coronaviruses circulating in bats in China, suggesting that bats are the most likely source of the ancestral virus of SARS-CoV-2.
But detection of VOCs in white-tailed deer long after their circulation in humans raises questions about whether deer, acting as a reservoir for the virus, could introduce the variants into other animal populations or even back into human populations. SARS-CoV-2 has also been detected in deer populations in Canada. The National Centre for Foreign Animal Disease in 2021 found deer in Quebec that appeared otherwise healthy were harbouring the virus.
"The findings are important in that they demonstrate that there is a risk of contact with infectious SARS-CoV-2 during handling and processing of white-tailed deer carcasses, which could lead to spillback via deer-to-human transmission of the virus," the authors wrote.
For this reason, the study's authors warn white-tailed deer populations should be monitored closely and that measures to minimize transmission of the virus between humans and animals are "urgently needed."