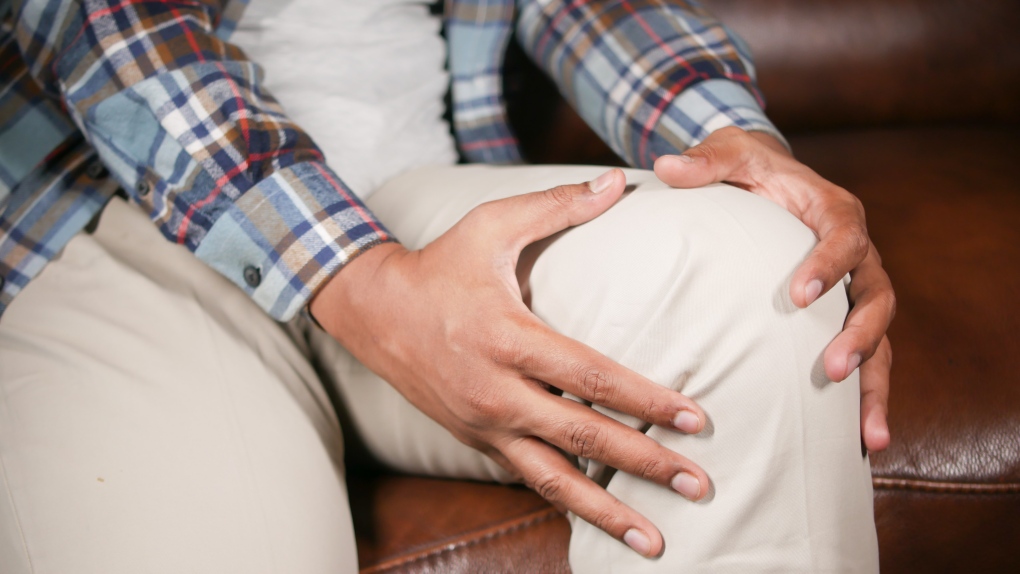
A common treatment for some arthritis pain might actually be making the condition worse, according to two new studies.
"Knee osteoarthritis is one of the most chronic, degenerative and progressive conditions, with an estimated incidence of 800,000 patients each year in the U.S. alone," said lead author of one of the studies, Dr. Upasana Bharadwaj.
Osteoarthritis is a common form of arthritis where the cartilage within a joint breaks down over time and the bones around it change, getting worse over time, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
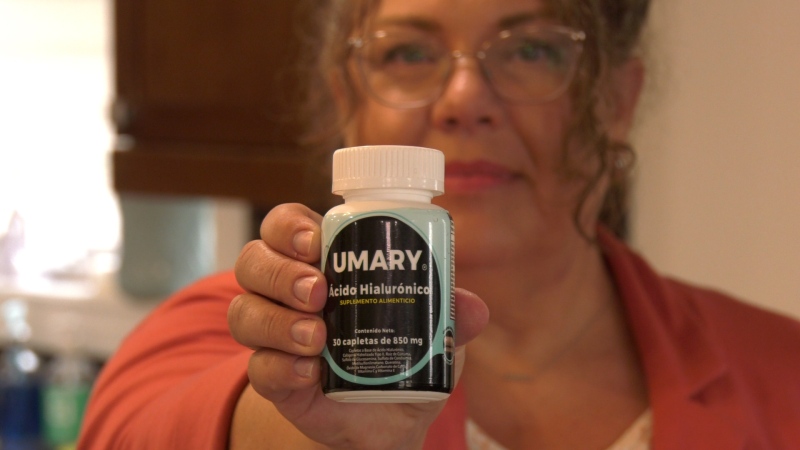
At least 10% of the patients in the study used injections to manage the pain, added Bharadwaj, who is a post-doctoral research fellow in the department of radiology at the University of California San Francisco's School of Medicine. Two of those pain management injectables are corticosteroids, the more common of the two, and hyaluronic acid.
The studies, which were presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America, used either radiograph or MRI images to track the progression of osteoarthritis in the knees of patients. Some of those patients didn't receive any treatment and others got corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections, according to the studies.
Both papers showed a statistically significant increase in progression of degenerative changes in knee cartilage over two years in people that had corticosteroid injections compared with those who had hyaluronic acid or no injections, according to the study authors.
However, just because the images might look worse doesn't always mean that the people are feeling more pain, said Azad Darbandi, lead author of the other study.
"You might see that the knee looks bad on a radiograph, but the patient might not be having worse symptoms," added Darbandi, a researcher and medical student at the Chicago Medical School of Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science.
The studies highlight a debate in the osteoarthritis scientific community about the role of changes in the structure of the joint. Currently, pain is the primarily recognized symptom, said Jason Kim, the Arthritis Foundation's vice president of osteoarthritis research. Kim was not involved in either study.
The takeaway from the studies is that corticosteroids should be administered with caution for osteoarthritis pain.
Hyaluronic acid injections may be a promising option for managing pain but is less utilized because there is less research, and most patients have to pay out of pocket, Darbandi said.
"Perhaps hyaluronic acid injections need to be studied for pain management more thoroughly," he said.
How to treat your osteoarthritis pain
Corticosteroids are a fast way to get pain relief and control inflammation but might not be a good option for long-term treatment, Kim said. Repeated injections can put patients at risk for other problems, such as infections because corticosteroids suppress your immune system, he said.
And some people may not see significant benefit from either steroid or hyaluronic acid injections, Kim added.
For a long-term strategy, Kim recommended building a trusted team of health care providers, including your primary care doctor, orthopedic specialist, physical therapist, nutritionist and rheumatologist.
It could be helpful to manage weight and body mass index, or BMI, to improve metabolic effects and reduce overall inflammation, Kim said. It's also important to try to exercise and be physically active, he said, adding that walking has been proven to improve arthritis.