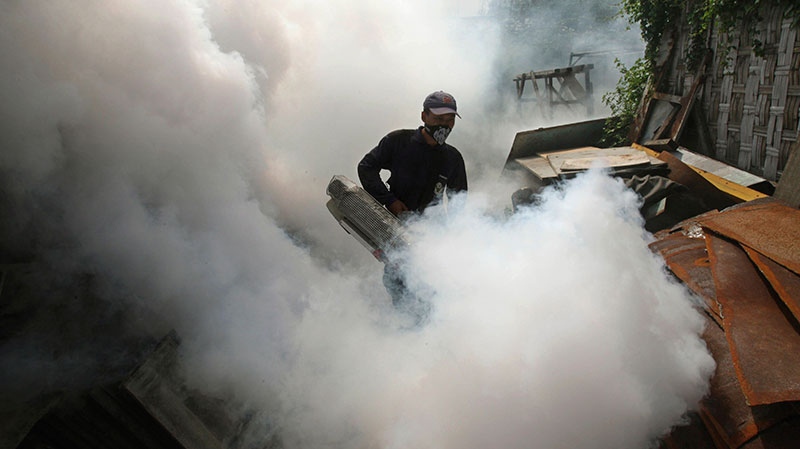
LONDON -- There may be nearly four times as many people infected with the tropical disease dengue globally than was previously believed, according to a new study.
The World Health Organization has estimated there are about 50 million to 100 million cases of dengue, also known as "break-bone fever," every year. But new research puts the number at around 390 million -- though about two-thirds of those people have only mild illness and don't need medical attention. The study was published online Sunday in the journal Nature.
The data won't change how patients are handled but could prompt a speedier search for a vaccine for the mosquito-borne disease. The study was funded by the Wellcome Trust, the U.S. Department of Homeland Security and others.
WHO said it wasn't surprised by the higher estimates. "We fully agree the spectrum of dengue is very wide and there was every chance we were missing cases," said Raman Velayudhan, the agency's global dengue co-ordinator. WHO was not involved in the new research.
"The new numbers are not out of the realm of what was expected," said Jeremy Farrar, director of the Oxford University Clinical Research Unit in Vietnam, one of the study authors. He said the figures came from analyzing more evidence than was used in the past and included other factors that influence dengue.
Dengue causes symptoms including fever and severe joint pains. The disease mostly affects people in Asia, Africa and Latin America though it has also recently popped up in parts of Western Europe and the U.S.
There are four kinds of dengue and catching it once doesn't ensure immunity; subsequent infections raise the risk of severe dengue and may include hemorrhaging. The death rate is usually below 1 per cent if patients get treated quickly, but can rise to 10 per cent if not.
Clarence Tam, an infectious diseases expert at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, said more research was needed on the significance of the nearly 300 million people who have mild dengue.
"Whether these cases are an important source of dengue infection for others is not well known," he said. "But there is clearly more dengue in the world than we thought."